- Navigating the AI frontier: Cybersecurity challenges and solutions

In an era where artificial intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing industries and our daily lives, new cybersecurity challenges have emerged. As AI systems become increasingly integrated into critical infrastructure, financial systems, and personal devices, robust cybersecurity measures are more pressing than ever. A recent comprehensive study published in the Computer Science & IT Research Journal sheds light on the complex interplay between AI and cybersecurity, offering both theoretical frameworks and practical solutions for addressing these challenges.
The double-edged sword of AI
AI technologies offer unprecedented capabilities for threat detection, automated response, and predictive analytics in cybersecurity. According to Dr. Babajide Tolulope Familoni, the lead author of the study, “Machine learning algorithms can sift through massive datasets to detect anomalies indicative of cyber threats, enabling rapid threat identification and response.” This capability allows organizations to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals, potentially thwarting attacks before they fully materialize.
However, integrating AI into cybersecurity also introduces new vulnerabilities. Adversarial machine learning, for instance, can be exploited by malicious actors to manipulate AI systems, potentially rendering them ineffective against sophisticated attacks. The study highlights the growing concern of AI-generated deepfakes, which pose significant threats to information integrity and can be weaponized for disinformation campaigns or identity theft.
Emerging threats in AI
The research identifies several key areas of concern in the evolving cybersecurity landscape:
- Adversarial attacks on AI systems
- Data privacy and confidentiality breaches
- Manipulation of AI-generated content (deepfakes)
- AI-enabled cyberattacks
- Vulnerabilities in AI-driven IoT devices
- Geopolitical implications of AI-powered offensive cyber capabilities
Dr. Ahmad Ibrahim, a co-author of the study, warns, “The proliferation of AI-driven IoT devices introduces new attack surfaces and vulnerabilities in interconnected systems. As the number of these devices grows exponentially, securing them against cyber threats becomes increasingly challenging.”
Solutions for AI cybersecurity
To address these multifaceted challenges, the research proposes a combination of theoretical approaches and practical strategies. Key theoretical frameworks include:
- Threat modeling for AI systems
- Adversarial machine learning analysis
- Secure multiparty computation
- Formal verification techniques
On the practical front, the study recommends:
- Implementing AI-powered threat detection and response systems
- Enhancing the resilience of AI systems through adversarial training
- Developing AI-specific security measures and best practices
- Investing in cybersecurity awareness and training programs
- Fostering collaboration and information sharing among stakeholders

Ethics and regulation in AI
The integration of AI in cybersecurity raises important ethical questions and regulatory challenges. Dr. Sontan Samuel, an expert in AI ethics cited in the study, emphasizes, “The deployment of autonomous AI systems for cyber defense raises questions surrounding accountability, transparency, and unintended consequences.“
The research calls for comprehensive regulatory frameworks that address data protection, ethical AI practices, and international cooperation in cybersecurity. It stresses the need for a balance between innovation and security, with flexible regulations that can adapt to rapidly evolving technologies and threats.
The human element in AI security
Despite the advanced capabilities of AI, the study underscores the critical role of human expertise in cybersecurity. Dr. Ronchi, a specialist in human factors in cybersecurity, notes, “Human oversight is vital to validate AI-generated insights, assess the severity of security incidents, and prioritize response actions based on business objectives and risk tolerance levels.“
The research recommends ongoing training and skill development programs to equip cybersecurity professionals with the knowledge needed to effectively leverage AI technologies in defense strategies.
Future directions for AI and cybersecurity
As AI continues to evolve, so too will the cybersecurity landscape. The study outlines several key areas for future focus:
- Developing robust defenses against adversarial AI
- Enhancing privacy-preserving AI techniques
- Improving the explainability and transparency of AI systems
- Addressing bias and fairness concerns in AI-powered cybersecurity solutions
- Building cyber resilience through adaptive defense strategies
A call for a holistic approach
The comprehensive analysis presented in this study serves as a wake-up call for organizations, policymakers, and cybersecurity professionals. As Dr. Familoni concludes, “Cybersecurity in the age of AI presents unprecedented challenges and opportunities that require a multifaceted approach. By embracing a holistic strategy that combines theoretical insights with practical solutions, we can harness the power of AI to enhance our cyber defenses while mitigating associated risks.“
As we stand at the crossroads of AI innovation and cybersecurity, the path forward demands collaboration, continuous learning, and a commitment to ethical practices. Only through such a concerted effort can we hope to secure our digital future in an increasingly AI-driven world.
Joe Shenouda Cyber-Consult.org
Sources:
- Familoni, B. T., et al. (2024). Cybersecurity Challenges in the Age of AI: Theoretical Approaches and Practical Solutions. Computer Science & IT Research Journal, 5(3), 703-724.
- Ahmad, I. A. I., et al. (2024). Cybersecurity challenges in smart cities: a case review of African metropolises. Computer Science & IT Research Journal, 5(2), 254-269.
- Sontan, A. D., & Samuel, S. V. (2024). The intersection of Artificial Intelligence and cybersecurity: Challenges and opportunities. World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, 21(2), 1720-1736.
- Ronchi, A. M. (2022). Human factor, resilience, and cyber/hybrid influence. Information & Security, 53(2), 221-239
- Unprotected University Computer in Czech Republic Leaves Network Vulnerable, Security Researcher Warns

Helmond, The Netherlands – In a cybersecurity snafu that raises serious questions about online safety, a university computer in the Czech Republic was left completely unprotected, potentially exposing the entire university network to hackers. Security researcher Joe Shenouda from Cyber Consult stumbled upon the glaring security hole while routine scanning for vulnerabilities in public networks.
The university in question, Brno University of Technology, is a distinguished institution known for its advancements in science and technology. The university’s network, a critical infrastructure for academic and research activities, was compromised by a single unprotected computer. Alarmingly, this computer lacked even basic authentication measures, essentially leaving the door wide open for anyone to waltz in.

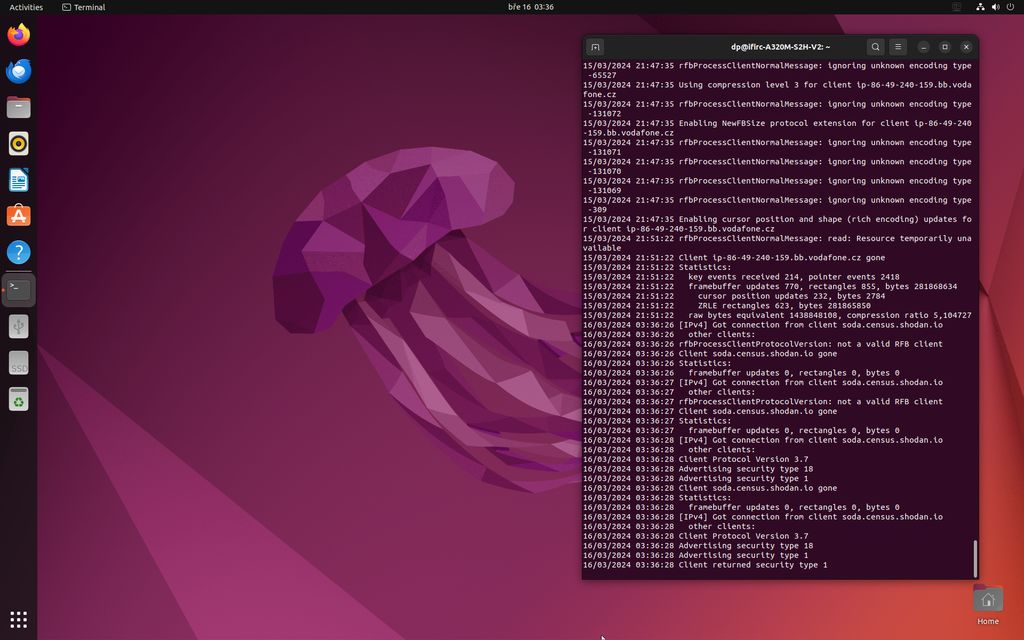
Shenouda’s investigation revealed several attempted connections to the vulnerable machine, with system logs indicating attempts to exploit the VNC protocol, a common method for remote desktop access. This suggests that malicious actors were actively targeting the unsecured computer as a potential gateway into the university’s broader network.
“The presence of an unprotected computer on a university network is a recipe for disaster,” says Shenouda. “Universities are treasure troves of sensitive data, and leaving a backdoor open like this is a major security risk.”

Shenouda responsibly attempted to contact Brno University of Technology to report the gaping vulnerability. Unfortunately, there has been no response from the university at the time of this publication. This lack of communication underscores the need for open channels between security researchers and organizations to swiftly address cybersecurity threats.
The incident serves as a chilling reminder of the cybersecurity vulnerabilities plaguing educational institutions worldwide. Universities are increasingly becoming targets for cyberattacks due to the wealth of intellectual property and complex networks they manage. This incident makes it abundantly clear that universities need to prioritize robust security protocols, continuous vigilance, and a proactive approach to safeguarding their digital assets.
The cybersecurity community will be closely monitoring Brno University of Technology’s response to this security breach. This situation also highlights the invaluable role that independent security researchers like Shenouda play in uncovering vulnerabilities and working towards a more secure digital landscape.
In the wake of this discovery, educational institutions everywhere are urged to take a good, hard look at their cybersecurity measures. Ensuring all devices and systems connected to their networks are properly protected is paramount. Collaboration between academia and security professionals is essential to building a safe and secure digital environment for education and research.
- The Road to a Passwordless Future

The cybersecurity landscape is undergoing a metamorphosis, driven by the inadequacy of traditional password-based security in the face of an ever-evolving threat landscape. This article delves into the technical rationale for a passwordless future, exploring the vulnerabilities of passwords and the compelling advantages offered by more sophisticated authentication methods.
The Achilles’ Heel of Passwords: A Technical Breakdown
Passwords, once the cornerstone of digital security, are demonstrably unfit for the complexities of the modern threat landscape. Here’s a granular dissection of their shortcomings:
- The Human Factor Flaw: Mnemotechnically-sound passwords are notoriously difficult to recall, leading to widespread password reuse and predictable choices (“password123”). These weak selections become fodder for brute-force attacks and password spraying techniques, enabling unauthorized access with alarming ease.
- Static Vulnerability: A compromised password grants unfettered access to all associated accounts until a change is implemented. This critical window of vulnerability offers attackers ample time to wreak havoc, deploy ransomware, or steal sensitive data.
- Centralized Storage Risks: Data breaches of password databases can lay bare millions of user credentials, highlighting the inherent insecurity of centralized storage. Credential stuffing attacks, where stolen passwords are used to gain access to other accounts, become a major concern.
Beyond the Security Breach: The Operational Burden of Passwords
The inefficiencies of password systems extend far beyond security vulnerabilities, creating significant operational headaches for organizations:
- IT Resource Drain: Managing complex password policies, enforcing multi-factor authentication protocols, and handling password resets and breaches consume valuable IT resources. The cost of password resets alone can be substantial for large enterprises.
- Usability Woes: Users often struggle to create and remember strong, unique passwords for a multitude of accounts. Inevitably, password fatigue sets in, leading to poor password hygiene practices.
A Brighter Future: Secure and Streamlined Authentication Beyond Passwords
The limitations of passwords necessitate a paradigm shift towards more secure and user-friendly authentication solutions. Here’s a closer look at some promising contenders:
- Biometric Authentication: Leveraging fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans offers a powerful layer of security. These unique biological characteristics are inherently difficult to replicate or steal. However, privacy concerns surrounding biometric data collection and storage require careful consideration and robust security protocols.
- Cryptographic Keys and PKI: Public key infrastructure (PKI) utilizes cryptographic keys for secure authentication, eliminating the need for passwords altogether. PKI offers a well-established security framework but necessitates a robust infrastructure overhaul and a behavioral shift for both users and organizations.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Hardware Tokens: MFA, by combining “something you know” (a PIN), “something you have” (a hardware token), and “something you are” (biometrics), significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. However, striking a balance between robust security and user experience is crucial for wider adoption.
Charting the Course: A Holistic Approach to a Passwordless Future
The transition to a passwordless world is a monumental shift in how we secure our digital identities. It necessitates a comprehensive approach that incorporates the following elements:
- Integration of Technological Solutions: Implementing secure authentication protocols like FIDO2 and WebAuthn will be paramount. These standards offer interoperability between different platforms and devices, ensuring a seamless user experience.
- Policy and User Education: Developing and enforcing strong password policies in the interim is crucial, while simultaneously educating users on robust password hygiene practices and the benefits of passwordless authentication.
- Cultivating a Security-Conscious Culture: Embedding a culture of security awareness within organizations is essential. This involves promoting best practices for password management, data handling, and a general vigilance against cyber threats.
Conclusion: A Secure and Seamless Digital Future
While challenges such as technology adoption rates and potential privacy concerns exist, a passwordless future is no longer a utopian ideal, but an essential step in fortifying our digital defenses. By embracing secure and user-centric authentication methods, we can create a future where digital security is both robust and seamless, empowering users and organizations to thrive in the ever-evolving digital landscape.
Joe Shenouda
- AI NIS2 Compliance Advisor

Introducing the NIS2 Compliance Advisor! 🚀 Navigating the complexities of the NIS2 Directive just got easier. My new AI-powered advisor is here to guide you through every step of achieving compliance with the directive. Whether you’re determining your entity category, implementing cybersecurity measures, or understanding legal obligations, this tool simplifies the process.
🌍 Multilingual Support: Understanding that NIS2 impacts organizations across various countries, our advisor is equipped to assist you in your preferred language.
🔍 Tailored Guidance: From risk management to incident reporting, get detailed and actionable advice tailored to your organization’s specific needs.
📅 Stay Ahead of the Deadline: With the October 2024 deadline approaching, our advisor ensures you’re on track to meet all requirements.
🔗 https://chat.openai.com/g/g-3wATfTwpg-nis2-compliance-advisor
Try the NIS2 Compliance Advisor now and experience hassle-free navigation of the NIS2 Directive.
NIS2Directive #Cybersecurity #Compliance #AI #Innovation
- The Human Element in Cybersecurity’s 2030 Landscape
Thank you, Top Cyber News MAGAZINE, for spotlighting me in the October 2023 issue! I’m honored to discuss the essence of humanity in cybersecurity, address the perceived “talent shortage,” and offer a glimpse into what 2030 might hold.


- October: The Month to Amplify Cybersecurity Awareness in Europe, with a Focus on NIS2

As a Dutch cybersecurity expert, I’ve witnessed the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity in Europe. This October, also known as Cybersecurity Month, I find it crucial to spotlight the importance of increasing cybersecurity awareness, especially given the new legislative frameworks such as NIS2.
The Cloud’s Cyber Resilience
Navigating cyber risks can be a labyrinth, even more so in the cloud. Cloud-native apps continuously evolve and scale, often at unprecedented speeds. Most businesses today utilize multiple cloud providers, leading to a flood of security notifications and an overwhelming array of security policies. There’s a pressing need for an integrated cloud security platform with a unified dashboard where policies can be adjusted to ensure consistent data protection. Harnessing such platforms provides a comprehensive security cover across public, private, and hybrid clouds, all manageable from a single dashboard.
The European NIS2 Directive
In this month of heightened awareness, it’s essential to go beyond recognizing threats. We must also focus on the latest legislative measures, such as the NIS2 directive. This directive is a significant stride towards bolstering Europe’s cybersecurity, especially for pivotal sectors like transportation, health, and finance. Companies within these sectors must be cognizant of their NIS2 obligations. The directive introduces mandatory reporting and due diligence, with leadership personally liable for any gross negligence. This highlights the criticality of adopting a proactive information security approach. Periodic risk assessments are indispensable.
Boosting Cyber Awareness through AI
In an era dominated by sophisticated cyber threats and criminals, fostering cyber awareness has never been more paramount. Traditional training modules often fall short in engaging employees, particularly when new threats demand immediate actions. Employing AI solutions, like AI-bot programs, provides a more holistic approach, including micro-learning sessions, on-the-job training with phishing simulations, and rapid, just-in-time learning. This multi-channel approach ensures a well-rounded, engaging learning experience for all.
Acknowledging Real Threats
While being aware of cyber threats is vital, it’s not the ultimate panacea. The human element remains vulnerable. Technical security measures are thus crucial. While minor security breaches might be unavoidable, their containment is essential. It’s equally vital to cultivate an environment where users feel secure enough to report any missteps they’ve made without the fear of being shamed.
Secure Access Protocols
The frequency of large-scale cyberattacks leveraging stolen or leaked employee credentials to infiltrate IT systems is alarmingly high. Yet, a staggering number of workers still employ insecure methods to manage their login details. As we mark this Cybersecurity Awareness Month, introducing professional, real-time password management solutions that store passwords securely, out of direct reach of employees, becomes paramount. This ensures timely identification, blockage, and prevention of identity-related threats.
Awareness as the Cornerstone of a Resilient Organization
Cybersecurity Month is an opportune time to re-focus on organizational cyber resilience. Tailoring security awareness training to specific departments or roles is essential, given that different departments face unique challenges. By integrating cybersecurity at a strategic level, it becomes part of the organization’s DNA, laying the groundwork for a response strategy and ensuring proactive rather than reactive measures. Given the rising costs and stringent conditions of cyber insurance, demonstrating robust security measures could even translate to premium discounts.
In conclusion, while October serves as a reminder, the journey of cybersecurity is year-round. With the introduction of directives like NIS2 and the increasing complexity of threats, it’s paramount for European businesses to remain vigilant and proactive.
Joe Shenouda
Dutch Cybersecurity Expert
#informationsecurity #cybersecurity #technology #innovation
- Cybergeddon: The Convergence of Cyberterrorism, Cyberwarfare, Cybercrime, and Hacktivism

Exploring the Threats and Implications of a Digital Apocalypse
🔒Cybergeddon is more than a buzzword; it’s a wake-up call for a digital doomsday scenario that could merge cybercrime, cyberwarfare, cyberterrorism, and hacktivism into a global crisis.🌍 #Cybergeddon #Cybersecurity
The term “Cybergeddon” combines two powerful concepts: “cyber,” referring to the realm of computers and digital networks, and “Armageddon,” which symbolizes an end-of-the-world scenario. The fusion of these words serves as a harrowing depiction of a massive, widespread disruption of digital infrastructure — one that merges cyberterrorism, cyberwarfare, cybercrime, and hacktivism. This is not a new idea, per se, but it has taken on a disturbingly concrete shape in recent years, evidenced by increasingly sophisticated cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructures like power grids, financial systems, and more. FireEye CEO Ashar Aziz has even warned that such attacks could severely destabilize not just the United States but the global economy as a whole.
The Perfect Storm: How Different Cyber Threats Converge into Cybergeddon
It’s crucial to understand that Cybergeddon is not simply an extension of existing cybersecurity challenges but a complex, multi-faceted event that combines distinct types of threats. Cyberterrorism aims to use digital means to instigate fear and violence for political or ideological ends. Cyberwarfare involves the strategic use of cyber capabilities by nation-states or international organizations against opponents. Cybercrime focuses on illegal activities that exploit computer systems for monetary or other personal gains. Finally, hacktivism is often driven by ideological motives to make a political or social impact through hacking. Cybergeddon is the scenario where these elements coalesce, amplifying the potential damage exponentially.
Economic and Industrial Targets: A Ticking Time Bomb
The economic implications of a Cybergeddon scenario are staggering. If large-scale sabotage targets key financial institutions, the ripple effects would traverse the globe, potentially causing economic collapse. Let’s consider an attack on Wall Street. If critical data becomes compromised or trading systems go offline, billions of dollars could vanish within minutes, leading to a domino effect that would affect stock markets worldwide.
Similarly, industrial control systems (ICS), which govern the likes of power plants, manufacturing units, and water supply networks, are another prime target. An attack on these systems could cripple vital services, plunging entire regions into chaos. The blackout in Ukraine in 2015, attributed to Russian hackers, serves as a case study in how fragile these infrastructures can be.
The Role of State Actors and Asymmetric Warfare
The concept of Cybergeddon also brings to light the role of state actors who may employ asymmetric warfare strategies. As conventional warfare has become increasingly costly and politically tricky, states may opt for cyber operations as a means of exerting influence or destabilization. North Korean attacks on Sony Pictures and the Russian interference in the 2016 U.S. presidential election are examples of how state actors can exploit cyber vulnerabilities for strategic objectives.
The EMP Threat: An Overlooked Component of Cybergeddon
The Defense Technical Information Center has flagged the possibility of nuclear electromagnetic pulse (EMP) attacks as a part of the military action that could precipitate Cybergeddon. EMPs have the potential to disable all electronic devices within their range of impact, essentially rendering every digital system useless. Such a situation would not only pave the way for conventional military attacks but would also create an immediate state of anarchy in the affected area, as all forms of digital communication would break down.
Mitigation and Preparedness: A Call to Action
So, how do we guard against Cybergeddon? The answer is not straightforward. The interrelated nature of these threats requires a comprehensive approach to cybersecurity that extends beyond the walls of any single organization. Governments need to strengthen their national security strategies to include robust cybersecurity protocols. Collaboration between nations becomes paramount to track and counter threats that easily transcend borders.
Companies, regardless of their size, must invest in advanced cybersecurity measures and cultivate a culture of awareness among employees. Cyber hygiene is not just an IT department’s responsibility; it’s a collective one. Plans for incident response and disaster recovery should be in place, tested, and updated regularly. Furthermore, public and private sectors need to work in unison to share intelligence and resources.
Conclusion
While Cybergeddon remains a theoretical concept, the evolving landscape of cyber threats lends it an uncomfortable air of inevitability. It is not enough to tackle cybercrime, cyberwarfare, cyberterrorism, and hacktivism in isolation. We must recognize the catastrophic potential that arises when these threats converge and act decisively to prevent a digital doomsday scenario. The cost of inaction is simply too high to ignore.
~ Joe Shenouda
- C2000 Police Communication System Vulnerable to Hacking and Failures

The Dutch Labor Inspectorate has raised serious concerns over the integrity and reliability of the C2000 communication system. Used widely by the police, emergency services, and parts of the Ministry of Defense, C2000 is paramount for inter-departmental communication, particularly in crisis situations.
However, long-standing grievances from police unions suggest the system often falls short, sometimes compromising officer and civilian safety. This concern was brought into sharp focus during a recent police chase in Rijsbergen, Noord-Brabant, due to communication failures. Such issues prompted the unions to seek intervention from the Labor Inspectorate.
In a detailed review by the Inspectorate, they found that the C2000 system exhibited weak coverage within buildings and identified 107 outdoor “problem areas” with inadequate radio coverage. Such issues could leave certain Dutch regions without crucial C2000 access, heightening risks during emergencies. Furthermore, the potential for system overloads in high-activity periods remains a concern, primarily due to excessive or misuse of the system.
However, it’s not just the system’s spotty coverage that’s problematic; inadequate training for officers on C2000’s operation also emerged as a major issue.
The malfunctioning system and training insufficiencies reportedly breach the Dutch Working Conditions Act. While the police cannot challenge these findings, they do have a fortnight to present their perspective. Post this period, the Inspectorate’s findings become conclusive, giving the police six months to bolster C2000’s coverage and three months to amplify training protocols.
Ramon Meijerink from the police union ACP hailed the decision, noting that it validates the union’s long-held concerns about the system’s inadequacies. Responding to the issue, police force management countered that they don’t exclusively lean on C2000 for safety, underlining that it effectively functions in 97% of instances, satisfying formal system criteria.
While the Inspectorate declared the alternative “Push to Talk system” unfit, there’s another alarming discovery to consider. Dutch researchers recently found that TETRA, C2000’s underlying radio technology, is highly susceptible to hacking, further threatening the system’s integrity and reliability.
In the age of increasing digital threats, it’s clear that the C2000’s vulnerabilities extend beyond mere coverage issues. Immediate interventions are imperative, not only for reliable communication but also to prevent potential cybersecurity breaches.
- Belgium’s Econocom Hacked

Belgium’s Econocom, a leading digital transformation company, has confirmed a cybersecurity attack that is currently under serious investigation and containment measures. The latest findings indicate that the leaked information originated from a third-party service provider working for a few Econocom clients in France. No internal systems or databases at Econocom have been affected, and there is no evidence to date of the disclosure of sensitive data.
On Sunday, August 20, a group of attackers claimed via a Twitter post to have hacked Econocom and began publishing data. No ransom demand has been received by the company. A formal complaint is being filed.
Upon learning of the incident, Econocom’s Group Security team and Security Operations Center immediately mobilized and initiated the first investigations. Initial findings did not reveal any malicious activities within Econocom’s Information Systems. The most plausible hypothesis was that the incident was a remnant of a previous attack in 2020, which had been contained.
On Tuesday, August 22, around 15:00 CET, Econocom noticed that more recent data had been exfiltrated and activated its cyber crisis management protocol. The exfiltrated data were found on two individual SharePoint folders (created via Teams). These folders contained minimal data and were isolated as soon as they were identified on Tuesday, August 22, 2023, at 16:00 and 18:00 respectively. All access to these SharePoint folders has been blocked. Econocom’s SharePoint infrastructure also prevents any form of propagation to other systems.
On the morning of Wednesday, August 23, investigations revealed that a user workstation from a third-party service provider in France was the likely source of the data leak. The service provider was immediately contacted to identify and block the source of the attack and assess its full impact. The staff of this service provider, who connect to an Econocom resource via VPN to retrieve necessary documents, have been identified, and their access to Econocom resources has been revoked. Investigations confirm that the leaked data originated from a shared space at the provider’s end.
As of now, the most plausible explanation is that the third-party service provider was compromised, and the data were exfiltrated from their infrastructure. However, investigations and containment measures continue at Econocom to ensure that no internal systems have been compromised.
Any significant new developments will be transparently communicated to all stakeholders, including relevant authorities.
Econocom Group SE is a European provider of business-to-business digital services.
- NIS2 Consultancy

NIS2 : Zit je met vragen over hoe je je OT/IT-systemen kunt afstemmen op de NIS2-richtlijnen? Of ben je benieuwd naar de aanvullende lokale beveiligingseisen die mogelijk van toepassing zijn? Neem contact met mij op voor vrijblijvend gesprek over NIS2 en wat het voor jouw bedrijf betekent.
– Identificatie van OT/IT-systemen die onder NIS2 vallen
– Een routekaart voor het voldoen aan NIS2-voorschriften
– Inzicht in de impact van NIS2 op je leveranciersHeb je specifieke vragen of uitdagingen rondom NIS2 en cybersecurity in jouw productieomgeving? Neem gerust contact met me op voor meer informatie.
#NIS2 #Cybersecurity #OT #IT #Compliance #Productiebedrijven #JoeShenouda #Nederland
——————————————————————————————
NIS2: Do you have questions about how to align your OT/IT systems with NIS2 guidelines? Or are you curious about the additional local security requirements that may apply? Contact me for a no-obligation conversation about NIS2 and what it means for your business.
- Identification of OT/IT systems that fall under NIS2
- A roadmap for complying with NIS2 regulations
- Insight into the impact of NIS2 on your suppliers
Do you have specific questions or challenges regarding NIS2 and cybersecurity in your production environment? Feel free to contact me for more information.
#NIS2 #Cybersecurity #OT #IT #Compliance #ProductionCompanies #JoeShenouda
- 30 Enlightening Quotes on Zero-Trust Security

- “Zero Trust is not a product or a service, it is a strategy to guarantee safety in the digital landscape.”
- “The beauty of Zero Trust is that it assumes everyone is a potential threat, thus it verifies everything.”
- “Zero Trust is like having a well-oiled lock on every door in your house, not just the front door.”
- “We have given up the boundaries of our network to the world of Zero Trust – everyone is inside, and everyone is outside.”
- “With Zero Trust, there is no place to hide from constant scrutiny and verification.”
- “In Zero Trust, it’s all about verification, not trust.”
- “Zero Trust is the digital equivalent of ‘trust, but verify’.”
- “Zero Trust does not mean there is no trust, it simply means we have to earn it.”
- “In the world of cyber security, the only certainty is Zero Trust.”
- “Zero Trust is not a technology you buy, but a philosophy you adopt.”
- “The reality of the digital world is that everyone is potentially dangerous. Hence, we need to turn to Zero Trust.”
- “Zero Trust is the logical evolution of cybersecurity in a world where boundaries are increasingly blurring.”
- “In the world of Zero Trust, it’s all about constant verification, no matter who you are or where you are from.”
- “Zero Trust acknowledges that traditional security approaches are inadequate in the face of advanced threats.”
- “Zero Trust is the new normal. It’s not a question of ‘if’, but ‘when’.”
- “In Zero Trust, it’s all about ‘no trust, only verification’.”
- “Zero Trust is about continually reconsidering and re-evaluating your security posture.”
- “Zero Trust is not about paranoia, it’s about realism in the world of cyber security.”
- “Zero Trust is like a traffic light that always stays red, unless explicitly verified otherwise.”
- “Zero Trust is the acceptance of the harsh reality that threats can come from anywhere.”
- “In the age of Zero Trust, it’s all about ‘who are you?’ and ‘what can you prove?’.”
- “With Zero Trust, even the smallest device can be a fortress.”
- “Zero Trust is not an end goal, but a continuous journey towards better security.”
- “In a world where trust is a luxury, Zero Trust provides a foundation of safety.”
- “Zero Trust begins where the illusion of a secure perimeter ends.”
- “With Zero Trust, every network is a fortress, and every user a potential intruder.”
- “Zero Trust is not about distrust, it’s about performing the right verifications.”
- “Trust can be breached, but Zero Trust is infallible.”
- “In the world of Zero Trust, we are all suspects until proven otherwise.”
- “The beauty of Zero Trust is that it puts everyone on the same level – always verified, never automatically trusted.”
Readers are welcome to use these insightful quotes on Zero Trust security, kindly remember to attribute them to Joe Shenouda
- Navigating the Complex Cybersecurity Salary Landscape

I recently analyzed an interesting dataset from Kaggle.com on cybersecurity salaries across the globe. The data was compiled from a survey hosted by salaries.infosec-jobs.com, and provides a useful glimpse into cybersecurity pay scales.
With over 1000 salary data points covering years 2020-2022, the dataset includes details on roles, experience levels, locations, company sizes and more. I filtered and aggregated this data to spot key trends and insights. For aspiring cybersecurity professionals, understanding these salary factors can help navigate a complex job market.
Based on my analysis, here are 9 key insights on cybersecurity salaries and careers… Read more on Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/navigating-complex-cybersecurity-salary-landscape-joe/
- Transforming EU Cybersecurity: The Impact of NIS2 on Your Organisation

Over the past few years, a range of developments, including COVID-19, issues in Ukraine, cybersecurity threats, and the consequences of climate change, have increasingly jeopardized the safety of our society and economy. In light of these developments, the European Union has been working since 2020 on the Network and Information Security (NIS2) directive. The directive aims to enhance the digital resilience of European Member States.
The NIS2 directive focuses on threats to network and information systems, such as cybersecurity risks. Its arrival is expected to contribute to greater European harmonization and a higher level of cybersecurity in companies and organizations. The NIS2 is the successor of the first NIS directive, also known as the NIB (Network and Information Security), which was incorporated into the Network and Information Systems Security Act (Wbni) in the Netherlands in 2016.
The Implications of the NIS2 Directive for Your Organisation
European Member States have until the end of 2024 to incorporate the directive into national legislation. This involves the implementation of a duty of care and a reporting obligation, which both public and private organizations within certain sectors must adhere to. The sections below summarise the obligations prescribed by the NIS2 directive and the sectors it will apply to, helping organizations visualize the obligations they may have to meet by the end of 2024.
Sectors and Organisations Covered by the NIS2 Directive
The NIS2 directive focuses on sectors already covered by the first NIS directive, as well as several new sectors. Therefore, the number of public and private organizations falling under the directive is set to increase. Organizations in the following sectors will be subject to the NIS2 directive:
- Annex 1 sectors: Energy, Transport, Banking, Infrastructure, Healthcare, Drinking water, Digital infrastructure, and ICT service managers.
- Annex 2 sectors: Wastewater, Government services, Space, ICT service management, Digital providers, Postal and courier services, Waste management, Food, Chemical substances, Research, Manufacturing/production.
Essential and Important Entities
A significant change from the first NIS directive is that organizations automatically fall under the NIS2 directive if they are active in one of the above sectors and can be characterized as ‘essential’ or ‘important’ entities based on the following criteria:
- Essential entities: These are large organizations active in a sector from Annex I of the NIS2 directive. An organization is considered large based on the following criteria: a minimum of 250 employees or an annual turnover of €50 million or more and a balance sheet total of €43 million or more.
- Important entities: These are medium-sized organizations active in a sector from Annex I and medium-sized and large organizations active in a sector from Annex II. An organization is considered medium-sized based on the following criteria: 50 or more employees or an annual turnover and balance sheet total of €10 million or more.
Generally, it is assumed that the disruption of services by essential entities would have a more significant disruptive impact on the economy and society than disruption at important entities. Essential entities fall under a more intensive supervision regime, with both proactive and reactive oversight of compliance with obligations. Important entities are subject to a lighter form of supervision, which only occurs retrospectively, such as in cases where there are indications of non-compliance with the law or an incident has occurred.
Does the NIS2 Directive Apply to SMEs?
Micro and small businesses are not generally covered by the NIS2 directive. However, the minister responsible for a certain sector can still choose to designate a micro or small business based on a risk assessment. For example, if their service is deemed crucial for the Dutch economy or society. In this case, these companies will be informed by the relevant ministry.
Moreover, some micro and small businesses do fall under the NIS2 directive. These are companies active as providers of trust services, as a top-level domain name registry, as domain name registration service providers or as providers of public electronic communication networks or public electronic communication services. These companies are automatically covered by the NIS2 directive. Government agencies from the above sectors are also automatically covered by the NIS2 directive.
Obligations of the NIS2 Directive
- Duty of Care: The directive includes a duty of care that requires entities to carry out a risk assessment themselves. They can then take appropriate measures to protect the information they use and ensure the continuity of their services as much as possible.
- Reporting Obligation: The directive stipulates that entities must report incidents to the regulator within 24 hours. These are incidents that could significantly disrupt the provision of the essential service. In the case of a cyber incident, it must also be reported to the Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT), which then provides assistance and support.
What Can Organisations Expect from the Government?
The NIS2 directive obliges Member States to support critical, essential, and important entities in improving their resilience to digital risks. Essential and important entities must be supported by a CSIRT with advice and assistance. The support from the government can further consist of information exchange, guidelines, and resilience-enhancing instruments, for example, for carrying out a risk assessment.
How Can Organisations Prepare?
Organizations can prepare for the duty of care and reporting obligations imposed by the NIS2 directive by taking the following steps:
Conduct Risk Assessments: Evaluate your network and information systems to identify vulnerabilities and areas that could be improved to mitigate potential threats.
Implement Cybersecurity Measures: Invest in robust cybersecurity tools and measures to secure your networks and data from potential cyber threats.
Train Staff: Offer regular training to all staff members to ensure they understand their roles in cybersecurity and how to spot and respond to potential threats.
Develop Incident Response Plans: These plans should outline the steps your organization will take in the event of a cybersecurity incident, including how to report such incidents within the stipulated time frame.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Monitor the effectiveness of your cybersecurity measures and regularly review and update them to respond to the evolving threat landscape.
By understanding the requirements of the NIS2 directive and taking proactive steps to meet them, your organization can significantly enhance its cybersecurity readiness and resilience. Furthermore, it will ensure your compliance with this directive, thus avoiding potential penalties and reputational damage.
Given the potential implications and challenges posed by the NIS2 directive, it may be advisable to engage the services of experienced cybersecurity professionals who can guide your organization through the process of achieving compliance.
While the NIS2 directive will impose additional requirements on affected organizations, it is an important step in securing the digital infrastructure and information systems across the EU. Ultimately, these regulations will help to safeguard the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of networks and information systems – which are increasingly vital to our daily lives and economic activities.
- Environment Variables: A Security Debate at PyCon Italia 2023

From the historic city of Florence, Italy, comes a new battle; not fought with swords, but with code and software architecture. The controversy surrounds the practice of using environment variables to store secrets in applications, which has been a topic of intense discussion at PyCon Italia 2023.
Mackenzie Jackson, a developer advocate at GitGuardian, takes us through the arguments both for and against this practice, following his presentation at the conference. He references Alexander Darby from Palo Alto Networks, who presented opposing viewpoints on this issue.
Environment variables are key-value pairs that can store vital data, such as API keys and secrets, database configurations, and more. They offer flexibility, allowing applications to adapt to various environments without code modifications. However, their use for storing sensitive data has raised security concerns.
Darby highlighted how an attacker, once gaining access to a system, often dumps all environment variables, which can expose crucial data. This access makes it easier for an attacker to move into different systems and escalate their privileges. The core argument here is that while the use of environment variables makes an attacker’s job easier, this stage of attack implies that the system has already been significantly compromised.
Jackson, however, advocates for the use of environment variables. He points out how they can reduce the risk of secrets being hardcoded and leaked in source code, a significant issue that environment variables can help prevent by centralizing secret storage in a single .env file.
In conclusion, the debate remains open. From a purely security-focused perspective, the use of more secure secrets managers is ideal, supporting Darby’s viewpoint. However, Jackson makes a compelling argument for the simplicity and effectiveness of environment variables in preventing basic security mistakes. Despite the heated discussions at PyCon Italia, one thing is clear – secrets management remains a challenging issue in cybersecurity, not only in Italy or Europe but worldwide.
- RVAsec 2023 – Virginia

RVAsec 2023, the largest cybersecurity conference in Virginia, convened security professionals to discuss key topics around improving our teams, chief information security officer (CISO) concerns, user security and more. The conference, held in Richmond, had 28 speakers addressing various aspects of security.
Andy Ellis delivered a keynote on improving team leadership, emphasizing the six ways poor management destroys productivity: exhaustion, exclusion, unwillingness, inability, ineffectiveness, and misalignment. His leadership improvement strategies fall under three categories: Support, Management, and Authority.
Mark Arnold of Lares Consulting presented his research on the top concerns for CISOs. According to Arnold, the top five issues that keep CISOs awake at night include poor asset management, emerging vulnerabilities, failing security tools, blind spots, and insecure configurations. Arnold suggested adopting a consistent threat modeling framework to address these concerns.
Adrian Amos shared his research on the history of security and the resistance to change passwords. Despite an alarming 30% of internet users experiencing breaches due to weak passwords, 13% still recycle their passwords across all accounts. However, multi-factor authentication (MFA) has proven extremely effective, blocking 99.9% of attacks.
Andrew Hendela suggested that software bills of materials (SBOMs) are not enough to ensure software security. Instead, he proposed the creation of a “Software Bill of Behaviors” to understand what software does versus what it is expected to do.
Overall, the conference was a platform for discussing methods to strengthen team leadership, improve security strategies, and understand user behavior to enhance cybersecurity.

- Tracking Mobile Phone Locations Using Silent SMS Messages

A group of researchers have discovered a method to estimate a phone’s location with 96% accuracy by exploiting the vulnerabilities in GSMA networks, which handle SMS messaging globally. The process involves a side-channel attack using SMS delivery reports, which can provide a sender with estimates of the recipient’s location based on the timings of these messages.
The attack targets almost all cellular networks, including 2G communication, which is commonly used for SMS. The attacker needs only the recipient’s phone number to execute this method. By sending multiple silent SMS messages (Type 0 messages that don’t alert the recipient) and studying the time differences between when these messages are sent and received, the attacker can estimate the recipient’s location.
The accuracy of this method increases with more precise data on the target’s whereabouts. However, there are limitations due to various factors that can affect empirical measurements in a real-world exploit.
In terms of countermeasures, modifying SMS timings, installing spam filters, or disabling silent messages can reduce the likelihood of such attacks. Disabling the feature that generates delivery reports could be the most effective preventative measure. After the discovery, researchers informed the GSMA, which is currently evaluating various preventative actions.
Full Article: https://www.securitynewspaper.com/2023/06/20/how-to-hack-track-anybodys-phone-location-via-silent-sms-messages/ | See more here: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2306.07695.pdf
- Banks Facilitating Criminal Hackers: A Growing Concern

In an era where technology has transformed the way we live, work, and conduct financial transactions, cybersecurity threats have grown exponentially. Criminal hackers, employing sophisticated techniques to exploit individuals and businesses, are thriving. A disturbing trend that has come to light is how established banking systems can inadvertently facilitate these activities.
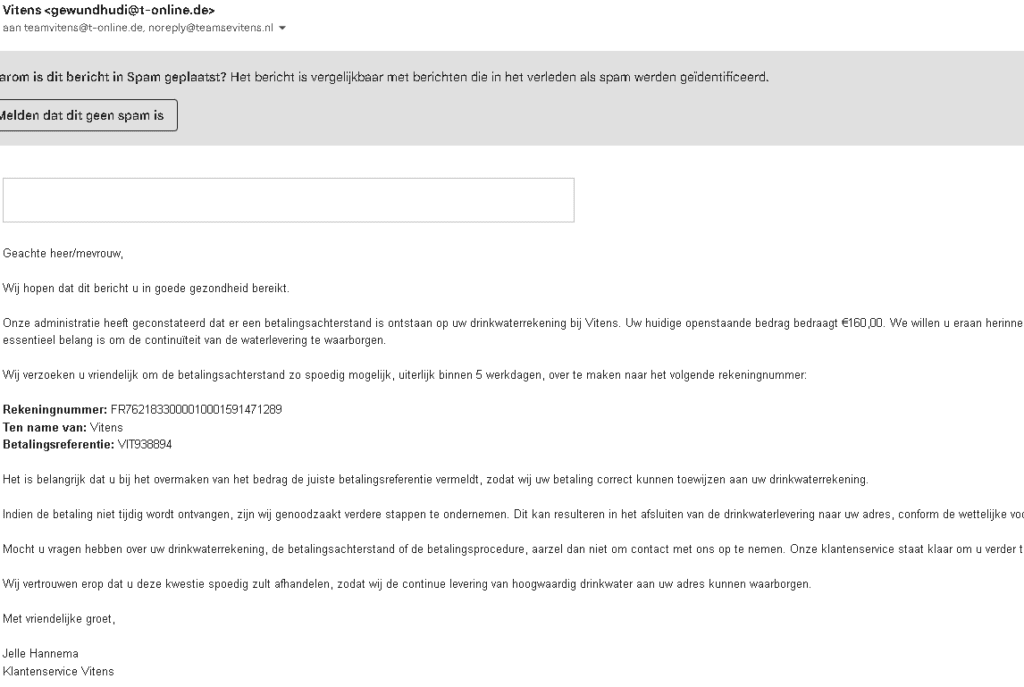
Recently, a case involving Vitens, the largest drinking water supplier in the Netherlands, and an Irish financial institution PFS Card Services Ireland Limited, serves as an alarming example of this issue. A fraudulent email, masquerading as an official correspondence from Vitens, was circulated among its customers. The email presented itself as a demand for payment, citing an outstanding balance on the customer’s water bill.
The bank account details provided in the email directed customers to make payments to an account hosted by PFS Card Services Ireland Limited, a low credit score / low trust financial institution, thereby lending an air of legitimacy to the scam.

Valid But Misleading
A surface-level check on the bank account details provided (FR7621833000010001591471289) shows that it is indeed a valid account. However, the name associated with the account, ‘Vitens‘, is misleading as it’s not associated with the actual company. The correspondence further used Vitens’ Executive, Jelle Hannema’s name, to appear more credible. This kind of ‘phishing’ scam is a common tactic used by criminal hackers, wherein they create a facade of legitimacy to trick victims into providing sensitive information or making unauthorized payments.
Facilitation by Financial Institutions
When hackers use established banks to run their operations, the banks unwittingly become facilitators of these criminal activities. The use of a valid bank account in this scam points towards a significant loophole in the banking industry’s verification and account monitoring systems.
Despite having stringent verification and monitoring mechanisms, these systems may not detect malicious activities promptly, thereby enabling scams to operate for longer periods and impact more victims. Even though the bank isn’t directly involved in the scam, it becomes an indirect facilitator by providing the infrastructure that allows such scams to flourish.
What Can Be Done?
Financial institutions must ramp up their efforts to stay ahead of these criminal hackers. This can include advanced identity verification during account creation, ongoing account activity monitoring, and swift action when suspicious activities are detected. They should also participate in cybersecurity awareness and education programs, advising customers on how to identify phishing scams and avoid falling prey to them.
Governmental and regulatory bodies must also step in to enforce stricter regulations and sanctions against banks that fail to prevent their platforms from being misused. As the world continues to move towards digital banking and online transactions, robust cybersecurity measures will only become more critical to ensuring the safety and integrity of our financial systems.
To conclude, the Vitens case underscores the growing concern of banks indirectly facilitating criminal activities. It is a call to action for all stakeholders involved – financial institutions, regulatory bodies, and individuals – to join forces in enhancing the digital safety of banking systems, to tackle the menace of cybercrime.
- EvilExtractor Data Theft Tool on the Rise in Europe

Researchers have observed an increase in attacks deploying the EvilExtractor tool, a data theft software targeting sensitive user information in Europe and the U.S. Sold by Kodex for $59/month, the tool boasts seven attack modules, such as ransomware and credential extraction. Although marketed as legitimate, it’s primarily promoted to threat actors on hacking forums.
- The Limitations of Microsoft Excel as a TARA Automation Tool in the Automotive Industry

Threat Assessment and Risk Assessment (TARA) is a critical process used by organizations to identify, assess, and prioritize potential risks. While many organizations rely on Microsoft Excel to automate TARA, it has significant limitations as the complexity of TARA increases. These limitations include:
- A descriptive approach that hinders effective risk management.
- Inefficiency in reusing previous work and best practices.
- Absence of version control.
- Scalability issues.
- Limited data visualization and modeling features.
- Difficulty in maintaining data integrity.
- Restricted integration abilities.
- Limited flow and process management.
- Inadequate collaboration and sharing capabilities.
- Incompatibility with automotive regulations and standards.
- Security vulnerabilities.
- Difficulty working with a DevSecOps extension.
To overcome these challenges, organizations should consider adopting proper tools and best practices tailored to their specific TARA needs.
- How-to guide: AWS security cheat sheet

Discover expert tips to bolster your #AWSSecurity and safeguard cloud workloads 🛡️! Learn about IAM policies, Control Tower, data protection, and more 🔒. #CloudSecurity #CyberRisk
In this blog post, we discuss various security measures and best practices to protect your AWS environment from potential cyber threats. These include implementing AWS IAM policies and permissions, using AWS Control Tower, managing accounts with AWS Organizations, implementing layered networking, ensuring compute infrastructure security, and protecting data with encryption and access controls. Additionally, we cover workload security, identity protection, and third-party integrations for enhanced AWS security, such as the Vulcan Cyber® risk remediation platform. By following these expert tips and best practices, you can reduce your attack surface and secure your cloud workloads effectively.
- Hacker sells stolen Quran Karim Radio content to Arab countries

Hacker steals content from Egyptian Quran Karim Radio through piracy program, sells to Arab & Islamic countries. Police investigate the case as suspect operates the program from his residence in Nile Delta. #Egypt #QuranKarimRadio #Piracy #Hackers
A hacker in Kafr el-Sheikh Governorate, Nile Delta, created a piracy program that allowed him to steal content from the Egyptian Quran Karim Radio. He then sold the content to subscribers in Egypt and Arab and Islamic countries. The hacker used his residence as a headquarters to manage and operate the application. Police are investigating the case.
- Modern Threat Vectors: Importance of Device-Centric Security

In today’s world, where work and personal computing are increasingly intertwined, it’s crucial to understand the importance of device-centric security. Traditional network-centric security models are becoming less effective as devices are used for various purposes, making them more vulnerable to threats.
Colin Rand’s blog post discusses the potential dangers of blurring the lines between work and personal computing, using a scenario where a child installs a seemingly harmless game mod on a parent’s work device, only to have it later become malicious. The post emphasizes the limitations of network-centric security and highlights the need for more comprehensive device-centric security.
Modern security models are shifting focus to consider the network as a mere connectivity tool, independent of the security model. This approach aims to stop and contain bad actors in a distributed world, rather than concentrating on malware “being on the network.”
The blog post also provides a detailed step-by-step breakdown of an attack, from initial setup to exploitation, and explains how multiple security tools are involved in addressing the threat. To minimize gaps in security, Rand suggests that an easy-to-deploy Secure Service Edge (SSE) platform is crucial.
In conclusion, as modern threat vectors continue to evolve, device-centric security is becoming increasingly important to protect both personal and enterprise data.
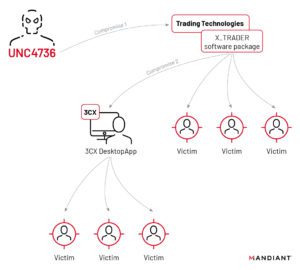
- 3CX VoIP Provider Hit by Unprecedented Double Supply Chain Attack: North Korean Group Targets Crypto Businesses

🔓 #3CX hit by a groundbreaking double #SupplyChainAttack! 😲 North Korean hackers target #Crypto businesses via a compromised employee’s PC. Stay vigilant and protect your systems! 💻🛡️ #CyberSecurity #VoIP #Malware #GopuramBackdoor
The recent supply chain attack on VoIP provider 3CX was made possible by an employee who fell victim to another supply chain attack. The employee had unknowingly installed a compromised official version of Trading Technologies’ software on their private computer. This revelation comes from a joint update provided by 3CX and cybersecurity firm Mandiant. According to Mandiant, this is the first time they have witnessed one supply chain attack leading to another.
3CX is one of the largest providers of business telephony solutions, claiming 600,000 customers and 12 million daily users. The company’s desktop application allows users to make calls and listen to voicemail from their desktops. Attackers were able to infect various versions of the software for macOS and Windows with malware.
Mandiant researchers discovered that the attackers gained access to 3CX through a compromised employee’s private computer, which had the X_Trader trading software installed from the official Trading Technologies website. The attackers had compromised Trading Technologies, allowing them to add a backdoor to X_Trader.
After compromising the 3CX employee’s private computer, the attackers stole login credentials and gained access to 3CX systems. Two days later, they were able to log in to the 3CX systems using the employee’s VPN connection. The attackers then intercepted other login credentials, moved laterally through the 3CX network, and eventually compromised the build environments for the macOS and Windows versions of the desktop application.
The malware added to the 3CX desktop application collects system and browser history information, which is sent to an attacker-controlled server. In a few select cases, the Gopuram backdoor was installed, granting the attackers access to the victim’s system. Antivirus company Kaspersky detected fewer than ten infections worldwide based on telemetry data from their clients.
According to researcher Georgy Kucherin, the primary malware and ultimate payload in the attack chain is the Gopuram backdoor, which has previously been used against crypto companies. The attackers behind the 3CX attack appear to have a specific interest in crypto businesses. Mandiant believes that a North Korea-based group is responsible for the attack.
Sources:
https://www.3cx.com/blog/news/mandiant-security-update2/
https://www.mandiant.com/resources/blog/3cx-software-supply-chain-compromise
- Critical Vulnerability in Microsoft Outlook: CVE-2023-23397 – How to Fix and Protect Your System

Protect your system from the critical CVE-2023-23397 vulnerability in Microsoft Outlook! Learn how to fix it and safeguard your information from potential attackers with Microsoft’s recommended solutions. #MicrosoftOutlook #cybersecurity #CVE-2023-23397
Microsoft has announced a critical elevation of privilege (EoP) authentication bypass vulnerability affecting all versions of Windows Outlook, called CVE-2023-23397. This zero-touch exploit can be triggered with no user interaction, and can result in an attacker gaining access to user information such as passwords or usernames. The vulnerability affects all supported versions of Microsoft Outlook for Windows, including Microsoft 365 Windows Outlook app. Microsoft has released a patch for the issue and recommends disabling WebClient service, adding users to the Protected Users Security Group, and enforcing SMB signing on clients and servers to prevent a relay attack. Microsoft has also provided a PowerShell script to scan emails, calendar entries, and task items to identify and remove the problematic “PidLidReminderFileParameter” property.
- Boost Your Software Development Lifecycle with CI/CD: Automating Updates and Deployments with Kubernetes and Popular Tools

Improve your software development with CI/CD! Learn how to automate updates and deployments with Kubernetes and popular tools like GitLab, Jenkins, CircleCI, and ArgoCD. #DevOps #ContinuousIntegration #ContinuousDelivery #Kubernetes
CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery/Deployment. It is a method that automates software updates at all stages of the software development lifecycle, delivering code fixes and new versions of the application without user intervention. CI involves building, testing, and merging new features to the app’s backend repository, while CD includes automated testing and uploading to the repository. Kubernetes can help automate the entire CI/CD process, from code commit to production deployment, providing a reliable and scalable platform for running applications. Popular CI/CD solutions include GitLab, Jenkins, CircleCI, and ArgoCD. Best practices for Kubernetes CI/CD include integration with git-based workflows, blue-green deployment patterns, and testing and scanning container images. Benefits of CI/CD include improved quality, faster product delivery, optimized testing and monitoring, greater agility, and measured progress.
- Think Before You Share: Preventing Data Breaches in SaaS Applications

“Collaboration in SaaS can create high-risk situations if links are shared without caution. Learn best practices for preventing data breaches and protecting your resources from @aryezacks’ latest article. #SaaSsecurity #datalossprevention #AdaptiveShield”
The article “Think Before You Share the Link: SaaS in the Real World” by Arye Zacks highlights the importance of being cautious when sharing links to SaaS applications. While collaboration is at the core of SaaS, sharing links can create a high-risk situation, leading to data leakage and loss. The author suggests best practices to prevent data breaches, such as sharing files with specific users, adding expiration dates to shared links, password-protecting all links, and creating a resource inventory. Additionally, an SSPM (Secure SaaS Privileged Management) solution, like Adaptive Shield, can help organizations identify and secure publicly shared resources. Overall, organizations should take necessary precautions to secure links and prevent data loss.
- Iranian Mint Sandstorm APT Linked to US Critical Infrastructure Attacks

Microsoft report links Iranian Mint Sandstorm APT to US critical infrastructure attacks, utilizing new tactics and targeting multiple organizations and individuals #cybersecurity #criticalinfrastructure #MintSandstormAPT
In a recent report, Microsoft has connected the Iranian Mint Sandstorm APT to a string of attacks aimed at critical infrastructure in the US from late 2021 to mid-2022. The group has refined its tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) by quickly weaponizing N-day vulnerabilities in enterprise applications using publicly disclosed POCs and custom tools. The group has targeted private and public organizations, including political dissidents, journalists, activists, the Defense Industrial Base (DIB), and employees from multiple government agencies, as well as individuals protesting oppressive regimes in the Middle East. The Mint Sandstorm group is also associated with other known groups, such as APT35, APT42, Charming Kitten, and TA453.
- Joint Advisory by UK NCSC and US Agencies: APT28 Exploits Cisco Routers in 2021

UK NCSC and US agencies issue joint advisory on APT28’s exploitation of Cisco routers in 2021, highlighting their sophisticated tactics and ties to Russian Military Intelligence Unit 26165 #cybersecurity #APT28 #FancyBear
The UK National Cyber Security Centre, the US National Security Agency, US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency, and US Federal Bureau of Investigation have released a joint advisory to outline the tactics, techniques and procedures used by APT28 to exploit Cisco routers in 2021. APT28, also known as Fancy Bear, STRONTIUM, Pawn Storm, the Sednit Gang and Sofacy, is a highly skilled threat actor believed to be the Russian General Staff Main Intelligence Directorate’s Military Intelligence Unit 26165.
- IT and Security – A Love Story

Breaking down barriers between IT and Security teams is key to a successful partnership. Learn how to align your priorities and work together towards a safer future. #ITsecurity #cybersecurity #collaboration
The article discusses the traditional rivalry between IT and security teams in organizations, which stems from their differing priorities. IT prioritizes stability and availability, while security focuses on locking down systems to reduce risks. However, the article suggests that these teams can learn to work together through various strategies, including justifying IT’s effort by explaining risk and potential impacts, defining operational processes for collaboration, agreeing on changes that improve security while minimizing procedure adjustment, educating IT on security, eliminating competition between IT security and operations, having ongoing conversations, ensuring security understands the network, collaborating to respond quickly to cyber incidents, and giving kudos when IT teams accomplish goals. When both teams align their goals and put the organization’s welfare first, they can have a successful partnership.
- DDosia: Uncovering Hacktivist Group NoName057(16)

Beware of NoName057(16)’s DDosia project – their cyber warfare activities threaten the safety of websites in Europe. Don’t support their cause by installing their tool, stay safe and secure online #Cybersecurity #DDoSattacks
NoName057(16) is a hacktivist group that uses their DDosia project to conduct DDoS attacks on websites of institutions and companies in European countries. They openly communicate that their actions are in support of Russia in the war against Ukraine and offer payments in cryptocurrencies to those who install their tool. Having their tool installed not only participates in cybercrime but also supports the group’s warfare activities. The group has released a more efficient Go variant of bots in late 2022, and the infrastructure for their DDoS attacks is largely static. SentinelLabs and Team Cymru have published investigations about the botnet architecture. Efforts are being made to detect and block DDosia to make the internet safer and mitigate the impact of DDoS attacks.
- Staying Ahead of State Hackers: The Dutch Challenge

Digital attackers are getting smarter, using existing tools on PCs to breach systems. The Netherlands is a prime target, facing constant attacks from Russia, China, Iran, and North Korea. #Cybersecurity #Netherlands
State hackers are increasingly using “living off the land” technology in their attacks, using existing tools on a PC. The Netherlands is a key country for hosting attack infrastructure and is frequently targeted by digital attacks from Russia, China, Iran, and North Korea. The European travel and aviation sector is a particular target. The AIVD warns that attacks on vital infrastructure can seriously disrupt society, a concern shared by other agencies.
- Secure Your Business with an Effective Vulnerability Disclosure Policy: The Ultimate Guide

Protect your business and build trust with customers and stakeholders by creating a comprehensive vulnerability disclosure policy! Our ultimate guide shows you how to do it right. #VulnerabilityDisclosure #Cybersecurity #EthicalHacking
Learn how to create a strong vulnerability disclosure policy with this ultimate guide. A vulnerability disclosure policy (VDP) allows ethical hackers to report security vulnerabilities to a company without fear of legal repercussions. A VDP offers many advantages, including streamlining the vulnerability reporting process and building trust with customers and stakeholders. The guide provides an overview of the key components of a VDP, including commitment, scope, safe harbor, process, preferences, and important guidelines. Following this guide will ensure that your VDP is comprehensive, unambiguous, and easy to understand for ethical hackers and security researchers.
- 9 Common GDPR Cookie Banner Blunders

Stay out of trouble and avoid hefty fines by avoiding these 9 common GDPR cookie banner mistakes! Check out our latest educational content for all the details. #GDPR #cookies #compliance
Author Jeffrey Edwards discusses nine common GDPR cookie banner mistakes that businesses make, which can lead to penalties, fines, and restrictions on data processing. These mistakes include not understanding the basic principles of GDPR, using cookie walls, relying on opt-out consent, using implied consent, using notice-only consent, tracking prior to consent, lacking the ability to withdraw or change consent, having no consent logs, and not regularly updating banners in line with regulatory changes.
- Chat Services Unite Against UK Online Safety Bill: A Threat to Privacy and Security

Privacy is not a privilege, it’s a basic human right. The proposed UK Online Safety Bill threatens to undermine that right for every British citizen and those they communicate with globally. We stand with other chat services in calling for a revision of this dangerous legislation. #PrivacyMatters #OnlineSafetyBill
WhatsApp, Signal, Threema, and other chat services have issued an open letter warning about a proposed UK law, the Online Safety Bill, which could undermine end-to-end encryption and pose an “unprecedented threat” to the privacy and security of all British citizens and those they communicate with globally. The proposed law could force chat services to monitor the messages sent by their users, which has been criticized by experts and civil rights movements. The chat services argue that it is impossible to monitor every chat message without undermining end-to-end encryption and that the proposed law would encourage hostile governments seeking similar legislation. They call on the UK government to revise the bill and encourage companies to provide more privacy and security for British citizens, not less.
- UK police forces reprimanded for unlawful recording of 200k phone calls via app

Privacy matters! Two UK police forces reprimanded for secretly recording 200k phone calls via an app without consent. #dataprotection #privacy #UKpolice
Two UK police forces have been reprimanded by the privacy watchdog ICO for recording 200,000 phone calls without informing those on the other end of the line. The app, which automatically recorded all phone calls, was launched in 2016 for a small group of officers, but Surrey and Sussex police made it available to all their staff. The ICO said more than 200,000 phone calls had been recorded, including those involving victims, witnesses and suspects. The app was subsequently deleted and all recordings, apart from those required for evidence, were destroyed. No financial penalties were issued.
- NCR’s Aloha POS System Affected by Ransomware Attack

Ransomware hits NCR’s Aloha POS system, affecting a subset of hospitality customers. Find out how the company is responding and restoring services. #NCR #AlohaPOS #RansomwareAttack
On April 12, NCR started investigating an issue related to its Aloha restaurant point-of-sale product. On April 15, the company confirmed that a limited number of ancillary Aloha applications for some hospitality customers were affected by an outage at a single data center due to a ransomware incident that was confirmed on April 13. NCR immediately contacted customers, engaged third-party cybersecurity experts, launched an investigation, and notified law enforcement. The company has been restoring affected services, but only specific functionality has been impacted, and restaurants should still be able to serve customers.
- APT29’s Cyber Espionage Campaign on NATO and EU Countries

New cyber espionage campaign targeting EU countries uncovered by researchers. Diplomatic entities and sensitive information systems among the targets. Stay informed on the latest cybersecurity threats. #cybersecurity #espionage #EU
Poland’s Military Counterintelligence Service and Computer Emergency Response Team have connected recent attacks on NATO and EU countries to the Russia-linked APT29 group. This group, also known as SVR group, Cozy Bear, Nobelium, and The Dukes, has previously been involved in cyber espionage, including the Democratic National Committee hack during the 2016 US Presidential Elections. In March 2023, a new cyber espionage campaign was uncovered by BlackBerry researchers, which targeted diplomatic entities and systems transmitting sensitive information about the region’s politics, aiding Ukrainian citizens fleeing the country, and providing help to the government of Ukraine.
- Access Control Benchmarks for SaaS Apps: Strengthening Your Security Posture

Improve your SaaS security posture with these access control benchmarks for Salesforce, Microsoft 365, and Google Workspace. Strengthen your first line of defense now! #SaaSsecurity #accesscontrol #cybersecurity
Access control is essential to SaaS security, accounting for 59% of all SaaS configurations. However, it is complex due to role-based access profiles required for different teams and employees. Access control benchmarks for Salesforce, Microsoft 365, and Google Workspace can help measure security posture. Salesforce’s SSO should be required, but only 2% of organizations do so. Microsoft 365’s legacy authentication protocols pose a risk, with over 80% of instances reviewed having at least one enabled. Google Workspace’s App Passwords bypass MFA and SSO, and should not be used by super admins. To strengthen access control, security teams can require SSO, enforce MFA, remove legacy protocols, and disable app passwords for super admins.
- Securing Infrastructure as Code (IaC) in DevOps: 15 Best Practices and Tools (+ Cheat Sheet)

Boost your #DevOps security with these 15 best practices and tools for securing Infrastructure as Code (IaC) throughout the SDLC. Check out our comprehensive guide and cheat sheet for easy reference. #IaCsecurity #DevSecOps
Learn how to secure your infrastructure as code (IaC) throughout the DevOps software development lifecycle with these 15 best practices and tools, from threat modeling to monitoring. This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights to improve the security, reliability, and consistency of your IaC, and the cheat sheet included makes it easy to reference. By following these guidelines, you can confidently adopt IaC in your DevOps processes without compromising the security of your applications and data.
- Embracing a Passwordless Future: How Advanced Authentication Methods are Revolutionizing Cybersecurity

Are you tired of constantly resetting passwords and worrying about cyber attacks? The good news is that the era of traditional password systems may be coming to an end. With a global shift towards passwordless authentication, cybersecurity is being revolutionized.
The benefits of passwordless authentication are numerous. First and foremost, it significantly increases security by utilizing multiple factors such as biometric data and tokens. This minimizes the risk of data breaches and cyber-attacks. Additionally, passwordless authentication enhances the user experience by simplifying authentication and eliminating the need for password resets or complex combinations. This, in turn, reduces IT support costs and improves access management. Finally, passwordless authentication is scalable and flexible, allowing organizations to adapt and scale to new technologies and users easily.
Innovations in passwordless authentication methods have also played a significant role in revolutionizing cybersecurity. Biometric authentication, multi-factor authentication (MFA), public key infrastructure (PKI), and single sign-on (SSO) are some of the cutting-edge methods being used today.
To implement passwordless authentication on a global scale, we need to raise awareness and education through campaigns, public education programs, and training sessions. Standardized protocols that integrate seamlessly with existing systems, applications, and devices need to be developed. Encouraging collaboration between governments, organizations, and industry groups can promote passwordless authentication adoption through incentives, regulations, and standards.
Of course, there are potential security risks associated with biometric authentication. But, these risks can be addressed through advanced encryption algorithms, liveness detection, and other cutting-edge technologies. Safeguarding systems with advanced firewalls and intrusion detection systems, continuously updating biometric data, and addressing privacy concerns can further minimize these risks.
In conclusion, passwordless authentication is the way forward, offering a more secure and convenient authentication system. With our collective efforts to adopt and implement advanced passwordless authentication methods, the future of cybersecurity is bright. So, let’s embrace a passwordless future and revolutionize cybersecurity.
- Centralized vs Decentralized Patch Management: Benefits and Comparison

Manage patches for multiple devices and apps from a single console with a centralized patch management system. Improve security, save costs, and ensure compliance. Learn more about the benefits and comparison with decentralized approach with JetPatch. #PatchManagement #ITSecurity
A centralized patch management system automates the process of managing patches for multiple devices and applications from a single console, reducing human error and increasing efficiency. It simplifies management, enhances security, saves costs, improves compliance, and provides better control and visibility. While decentralized patch management offers more flexibility, reduced network traffic, and lower risk of failure, the choice between the two depends on the organization’s needs. JetPatch offers a hybrid approach that combines the benefits of both centralized and decentralized patch management. As a leading provider of centralized patch management systems, JetPatch streamlines the patching process, reduces the risk of cyber attacks, and ensures compliance with industry regulations and standards.
- 9 Common CPRA Compliance Mistakes Businesses Must Avoid in California

CPRA compliance is crucial for businesses serving California residents. Avoid common mistakes and prepare for upcoming changes to protect consumer data and stay compliant with California privacy laws. #CPRA #PrivacyCompliance #CaliforniaPrivacy
The California Privacy Rights Act (CPRA) is set to take effect in 2023, and businesses must understand and adapt to its changes to avoid significant fines and legal action. Many businesses struggle with compliance under the existing California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), leading to common mistakes such as misunderstanding applicability, failing to provide “Do Not Sell” and “Limit the Use of My Sensitive Information” notices, inadequate opt-out methods, neglecting to obtain consent for selling or sharing children’s data, insufficient employee training, third-party vendor management, record-keeping, and not preparing for the CCPA’s replacement. By addressing these mistakes and preparing for the CPRA, businesses can comply with California privacy laws and protect consumer data.
- Why WhatsApp May Consider Leaving Europe in Light of New EU Regulations

Will WhatsApp and iMessage comply or leave the European market? The EU’s Digital Markets Act could have significant implications for messaging apps. Read more: #DigitalMarketsAct #messagingapps #EUregulations
The recent agreement between the European Parliament and the European Commission on the Digital Markets Act could have significant implications for messaging apps like WhatsApp and iMessage. The Act stipulates that these large messaging services must offer interoperability with smaller platforms when requested by them. This means that users of smaller messaging platforms will be able to exchange messages and files with users of the larger services.
While this move is intended to increase consumer choice, it could have significant implications for the way in which messaging services operate. It is likely that the larger messaging services will be reluctant to comply with these requirements, as they will need to make significant changes to their existing systems in order to offer interoperability with smaller services.
One possible outcome of this move is that the larger messaging services could choose to leave the European market altogether. While this would be a drastic step, it is not without precedent. In 2014, Google shut down its news service in Spain after the Spanish government introduced a law requiring news aggregators to pay for the use of news articles. Similarly, in 2018, the GDPR caused many small businesses to shut down or relocate outside the EU due to the increased regulatory burden.
If WhatsApp and iMessage were to leave the European market, this would have significant implications for millions of users across the continent. It would also represent a significant blow to the European tech industry, which is already struggling to keep up with its counterparts in the United States and Asia.
In addition, the move could have wider implications for the global tech industry. Other countries could follow the EU’s lead and introduce similar regulations, which could lead to further fragmentation of the messaging market. This could be particularly problematic for users who rely on messaging services to communicate with friends, family and colleagues across borders.
In conclusion, while the Digital Markets Act may be well-intentioned, it could have unintended consequences for the messaging market in Europe and beyond. It remains to be seen how the larger messaging services will respond to these requirements, and whether they will choose to comply or withdraw from the market altogether.
- Kubernetes 1.27 Release: Enhancements and Security Updates

Check out the latest Kubernetes 1.27 release! This update brings new security features and enhancements to help optimize your containerized applications. #Kubernetes #containerization #securityupdates #devops
The Kubernetes 1.27 release includes enhancements and security updates to provide an improved, more flexible, and secure platform for building and managing containerized applications. Among the enhancements are improvements to security with the ability to use seccomp by default, which limits the system calls that containers can access, reducing the attack surface. Other enhancements include pod scheduling readiness, match conditions for CEL in admission policy, Auth API to get Self-User attributes, and auto-refreshing CVE feed now valid JSON & Atom. The old Kubernetes container registry is no longer updated, and users need to update to registry.k8s.io. The enhancements offer a more expressive and efficient way to define policy webhook triggers, simplify configuration, and optimize the execution of admission control policies. Overall, the updates can help users optimize their Kubernetes workloads and build more resilient, secure, and efficient applications.
- GitHub’s Recent Private SSH Key Exposure: Risks, Remediation, and Prevention

GitHub’s recent SSH private key exposure is a wake-up call for all developers to stay vigilant about their security practices. Learn more about the risks and how to prevent similar incidents from happening again. #GitHub #cybersecurity #SSHkeyexposure
GitHub recently reported that its RSA SSH private key was briefly exposed in a public GitHub repository. The company explained that the key was only used to secure “Git operations over SSH using RSA” and no internal systems, customer data, or secure TLS connections were at risk. GitHub reacted immediately by changing the key.
This incident is further evidence that secrets sprawl is not only being driven by inexperienced developers or new teams but is affecting companies of all sizes. Leaked private SSH keys can lead to a “man-in-the-middle attack,” where the end user cannot tell the difference between the legitimate other party and the attacker. GitHub’s rotation of their private SSH key means workflow runs will fail if they are using actions/checkout with the ssh-key option. In such cases, developers will have to remove the old key or manually update their ~/.ssh/known_hosts file.
- Hyundai Data Breach Affects Customers in Italy and France: Personal Data Compromised

Personal data of Hyundai customers in Italy and France compromised in a recent data breach. Stay vigilant and protect your information! #Hyundai #databreach #cybersecurity
Hyundai has suffered a data breach that affects customers in Italy and France, as well as people who booked a test drive. The company warned that personal data has been compromised and hackers have gained access to it. Hyundai is a multinational car manufacturer that sells more than half a million vehicles annually in Europe, with a 3% market share in France and Italy.
- Galil Sewage Corporation Recovers from Cyberattack Causing Disruption to Irrigation Process

Galil Sewage Corporation overcomes cyberattack causing irrigation disruption. System back in operation after a day. #Cybersecurity #JordanValley #IrrigationDisruption
The Galil Sewage Corporation, which operates systems for monitoring irrigation and wastewater treatment in the Jordan Valley, experienced a cyberattack that blocked several controllers. The attack caused a disruption in the irrigation process, and it took the company’s experts an entire day to recover the system’s operations. The source of the attack is still unknown. The Jerusalem Post reported that the management worked throughout Sunday morning to resolve the issue and bring the systems back into full operation.
Read more: https://securityaffairs.com/144643/hacking/cyber-attacks-controllers-for-irrigating.html
- Spanish Authorities Arrest Notorious Hacker ‘Robin Hood’ for Alleged Theft of Sensitive Taxpayer Data

Spanish ‘Robin Hood’ hacker arrested for stealing sensitive taxpayer data. Expertise in money laundering & cyber assets led to his downfall. #Cybersecurity #HackerArrest #Spain
Jose Luis Huertas, also known as Alcasec and Mango, has been arrested in Madrid, Spain for allegedly stealing sensitive data of over 575,000 taxpayers from the national revenue service. The 19-year-old hacker is known as the “Robin Hood of Spanish Hackers” for his reputation of stealing from the rich and giving to the poor. He is considered one of the country’s most notorious hackers with expertise in money laundering and cyber assets. Spanish law enforcement authorities apprehended Huertas after tracking the cryptocurrency wallets he used to make payments for servers storing the stolen data, discovering more than $543,000 worth of crypto in the wallet he allegedly controlled. Huertas remains in custody as the judge has deemed him a flight risk.
Read more: https://www.hackread.com/alcasec-hacker-spanish-hackers-arrested/
- Ransomware Gangs Targeted UK: Education Sector and NHS Among the Victims

Ransomware gangs hit UK hard: education sector and NHS among the victims. Royal Mail faces largest ransom demand ever. Learn more in our latest article. #ransomware #cybersecurity #UK
The UK was a prime target for ransomware gangs between April 2022 and March 2023, with the country being the second most attacked in the world during this period. The Royal Mail was hit with an $80 million ransom demand, which is the largest known demand ever. The education sector was hit particularly hard, and the UK was a target for Vice Society, which focuses on attacking educational institutions. In August 2022, a ransomware attack on IT supplier Advanced caused widespread outages across the UK’s National Health Service (NHS), affecting various services, including patient referrals, ambulance dispatch, out-of-hours appointment bookings, mental health services, and emergency prescriptions.
Read more: https://www.malwarebytes.com/blog/threat-intelligence/2023/04/ransomware-review-uk
- New European Anti-Money Laundering Directive Raises Privacy Concerns Among Regulators

European privacy regulators express concern over new anti-money laundering directive allowing sharing of personal data. Learn more about the potential impact on citizens and the call for legislative action. #privacy #AML #dataprotection
European privacy regulators, united in the EDPB, have expressed concerns about a new European anti-money laundering directive that is being developed, which could have serious consequences for European citizens. The proposed provisions would allow private companies and public authorities to share personal data with each other, including transaction and personal data collected for customer research and transaction monitoring. This could lead to people being placed on blacklists and excluded from financial services. The EDPB has called on European legislators not to include these provisions in the final proposal for the law, citing concerns about legality, necessity, and proportionality. The Authority for Personal Data has also raised objections to such provisions in Dutch legislation.
- Cybersquatting Uncovered: How to Protect Your Brand and Digital Assets

Protect your brand’s online identity from cybersquatters! Learn the definitive guide for detection and prevention in our latest blog post. #cybersecurity #brandprotection.
Cybersquatting is a type of digital copyright and trademark infringement where someone registers a domain name or website address identical or similar to a targeted business, with the goal of confusing or tricking competitors and consumers into believing that the domain name is associated with a notable corporate brand or person. This can cause legal, financial, and reputational damage to businesses, but can be prevented through the right strategies. Common types of cybersquatting include typosquatting, brandjacking, cyberpiracy, and domain kiting.
Cybersquatters can register domains that are close to or nearly identical to many well-established brands to trick website browsers into making purchases from fake sites, leading to financial loss and reputational damage for both businesses and consumers.
Read more
- Securing America’s Digital Future: A Comprehensive Review of Biden-Harris Administration’s National Cybersecurity Strategy

Protecting critical infrastructure, disrupting threat actors, and promoting cybersecurity workforce development – dive into the five pillars of the Biden-Harris Administration’s National Cybersecurity Strategy to secure America’s digital future. #cybersecurity #digitalinfrastructure #BidenHarris
The Biden-Harris Administration has recently announced the National Cybersecurity Strategy, a comprehensive plan to safeguard the digital infrastructure of the United States and protect its citizens online. The strategy focuses on five main pillars, which include defending critical infrastructure, disrupting and dismantling threat actors, shaping market forces to drive security, investing in a resilient future, and forging international partnerships. It also calls for a shift in responsibility, where the most capable actors in the public and private sectors assume a greater share of the burden in mitigating cyber risks.
The strategy has critical objectives, such as protecting critical infrastructure, strengthening federal cybersecurity, promoting innovation and investment in cybersecurity, and advancing international cooperation. Additionally, key highlights of the strategy include initiatives to enhance supply chain security, improve incident response and recovery, promote cybersecurity workforce development, and strengthen partnerships with the private sector.
Overall, the National Cybersecurity Strategy represents a comprehensive approach to address the evolving cybersecurity threats facing the United States. It showcases the Biden-Harris administration’s commitment to safeguarding Americans in the digital age.
- Information Security and Cybersecurity: Understanding the Differences

In today’s digital age, information and cybersecurity are two essential concepts critical to any organization’s success and survival. While these two terms are often used interchangeably, there are some important differences between the two that are worth understanding.
Information security is a broader concept encompassing all aspects of protecting information, whether it’s stored physically or digitally. It involves implementing various measures to safeguard the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information, as well as protecting it from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, or destruction.
Information security encompasses a wide range of areas, including physical security (e.g., locks, access controls, surveillance systems), technical security (e.g., encryption, firewalls, intrusion detection systems), and administrative security (e.g., policies, procedures, and training). It is a proactive approach to managing risks associated with information and data, and it involves identifying and mitigating potential threats before they occur.
Cybersecurity, on the other hand, is a specific subset of information security that focuses on protecting computer systems, networks, and devices from digital attacks. Cybersecurity measures are designed to prevent, detect, and respond to threats that originate from cyberspace, such as malware, ransomware, phishing, and hacking.
Cybersecurity involves using various tools and techniques to protect networks and devices from unauthorized access or exploitation. These tools may include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, and encryption technologies. Cybersecurity also involves regularly monitoring networks and systems for suspicious activity and responding to incidents promptly to minimize damage.
In summary, information security and cybersecurity are closely related terms, but they are not the same thing. Information security is a broad term encompassing all aspects of protecting information. At the same time, cybersecurity is a specific subset of information security that focuses on protecting computer systems and networks from digital attacks. Both concepts are critical to the success and survival of any organization in today’s digital age, and they require a comprehensive and proactive approach to managing risks and threats.
PS: Investing in a Chief Cybersecurity Officer (CCO) in addition to a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) is highly recommended for organizations of all sizes.
- Top 8 Cloud Application Threats for European Businesses in 2023

This blog post discusses the top 8 threats to cloud applications in 2023, focusing on Europe. Companies with digital business strategies are living in an increasingly cloud-first world, but there are growing security issues introduced by the cloud that many organizations are not well equipped to address.
- The Vulkan Files: Explosive Leaked Documents Reveal Development of Global Cyber Weapons

Whistleblower leaks sensitive documents uncovering the development of offensive cyber tools, including those used in global cyber operations. #cybersecurity #leak
A whistleblower has leaked sensitive documents related to the development of offensive cyber tools by NTC Vulkan, a Moscow-based IT contractor firm. The documents describe the development of hacking tools for not just Russian military and intelligence agencies but also for the Russia-linked APT group Sandworm. The leaked documents, known as The Vulkan Files, cover details of three projects – Scan, Amesit, and Krystal-2B – and reveal the tools used in several global cyber operations, including the blackout in Ukraine, the development of the NotPetya malware, and the attacks on the Olympics in South Korea. These projects point toward a common set of goals of strategic information confrontation via cyber operations.
Read more: https://www.theregister.com/2023/03/31/vulkan_files_russia/
- CryptoClippy: The Malware Campaign Targeting Portuguese Speakers’ Cryptocurrency Wallets

A malware campaign called CryptoClippy has been discovered by Unit 42, which aims to steal cryptocurrency from legitimate users’ wallets by replacing their actual wallet address with a threat actor’s. The malware, known as a cryptocurrency clipper, monitors the victim’s clipboard for signs of cryptocurrency wallet addresses being copied. To deliver the malware, threat actors used Google Ads and traffic distribution systems to redirect victims to malicious domains impersonating the legitimate WhatsApp Web application. The campaign targets Portuguese speakers, and victims have been found across the manufacturing, IT services, and real estate industries. Palo Alto Networks customers are protected against this campaign through Cortex XDR.
Read more: https://unit42.paloaltonetworks.com/crypto-clipper-targets-portuguese-speakers/
- Beware of the Wi-Fi Queues: Researchers Find Ways to Bypass Wi-Fi Encryption

Researchers show how Wi-Fi encryption can be bypassed by manipulating transmit queues.
Researchers from Belgium and the US have discovered that active adversaries may be able to shake loose queued-up network packets from some access points by manipulating transmit queues. The queued-up data was stored in decrypted form and was anticipated that it might need to be re-encrypted with a new session key for delivery later on. The researchers figured out various ways of tricking some access points into releasing those queued-up network packets without any encryption at all or encrypted with a new session key that they chose for the purpose. Access point developers have been advised to use the 5.6 kernel.
To read the complete article see: https://nakedsecurity.sophos.com/2023/04/03/researchers-claim-they-can-bypass-wi-fi-encryption-briefly-at-least/
See full research here: https://papers.mathyvanhoef.com/usenix2023-wifi.pdf
- UK Honeypot Sting Exposes Thousands of Suspected Cyber Criminals in Global Crackdown

The UK’s National Crime Agency (NCA) has exposed the identities of thousands of suspected cyber criminals after a successful honeypot sting. The operation was part of an international effort to crack down on DDoS-for-hire services. #cybersecurity #DDoS #crime
The National Crime Agency (NCA) in the UK has exposed the identities of thousands of suspected cyber criminals who fell for a honeypot sting. The sting formed part of Operation Power Off, an international effort to clamp down on cyber criminals using Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) tactics. The NCA created several fake DDoS-for-fire websites to attract potential cyber criminals, which were accessed by several thousand people. The NCA collected the details given by prospective customers to access criminal services and will use them to target criminals. The operation took down sites that carried out over 30 million attacks in recent years.
- Winter Vivern Cyber Spy Gang Targets US and European Lawmakers with Unpatched Software

A persistent cyber gang is using unpatched software to target high-profile officials in the US and Europe. Stay vigilant and keep your systems up-to-date to protect against these evolving threats. #cybersecurity #APT #phishing
A pro-Russian cyber spy gang known as Winter Vivern has been targeting elected officials and their staff in the US, as well as European lawmakers, using unpatched Zimbra Collaboration software. The group, also known as TA473 and UAC-0114, has been active since December 2020, and previously targeted government agencies in Azerbaijan, Cyprus, India, Italy, Lithuania, Ukraine, and the Vatican. In recent campaigns, the gang has focused on Ukraine, Poland, Italy, and India, and has used phishing campaigns to trick targets into downloading malware-laden documents. The group’s persistent approach to vulnerability scanning and exploitation has been a key factor in its success.
Read more: https://www.theregister.com/2023/03/31/winter_vivern_european_goverments/
- Twitter’s leak illustrates why source code should never be sensitive

Twitter’s internal source code was recently leaked on a public GitHub repository by a user named FreeSpeechEnthusiast. The leak could be accidental or malicious, but the user’s name suggests a possible motive. The leak poses various risks, such as exposing secrets, logic flaws, and application architecture. Twitter has requested identifying information from GitHub to take legal action. To prevent source code from becoming a security risk, it is better to assume that it will be leaked and take appropriate measures.
- Cybersecurity Breach Strikes UK Criminal Records Office, Disrupting Operations

The UK Criminal Records Office (ACRO) experienced a cybersecurity incident, causing it to take down its customer portal and disrupting several operations, including police certificate procurement processing. ESET’s global security advisor and Kevin Beaumont, Head of Security Operations Centre at Arcadia Group Ltd, believe that ACRO has suffered a ransomware attack. The agency suspects that data, including identification and criminal conviction information, had been compromised during the two-month-long security breach. Since its website is down, the agency has to process police certificate applications manually by email. ACRO is working with national agencies to investigate the incident.
Further reading: https://www.hackread.com/uk-criminal-records-office-ransomware-attack/
- Ransomware + Healthcare: A Deadly Combination

In today’s digital age, ransomware attacks have become a major threat to businesses and organizations across all industries. However, the healthcare industry is particularly vulnerable, as it not only jeopardizes the availability of critical information and systems, but also puts patients’ privacy and safety at risk. This article explores the intersection of ransomware and healthcare, highlighting the risks and suggesting measures to safeguard healthcare systems.
Ransomware presents a triple-threat to healthcare: availability, confidentiality, and compliance. Availability is directly impacted by ransomware attacks, which can cause information and systems to become unavailable, hindering patient care. Confidentiality is also at risk, as ransomware has evolved into “blackmail-ware,” where sensitive data is held hostage until a ransom is paid, compromising patients’ right to privacy. Furthermore, a ransomware infection in healthcare is likely a HIPAA-reportable event, and if the PHI (protected health information) has been compromised, it must be reported to HHS (Department of Health and Human Services) and the affected individuals.
The evolution of ransomware has led to a more sophisticated business model, where ransomware is delivered as a service (RaaS), with separate creators, distributors, and customer service divisions. Customized ransoms and negotiations have become commonplace, along with the stealing of data before encryption. Ransomware negotiators are now professional services, adding to the complexity of ransomware attacks.
The healthcare industry has been affected by a significant number of ransomware attacks. In 2020 alone, there were 92 ransomware attacks on 600 organizations, compromising 18 million patient records, resulting in $20.8 billion in ransom, downtime, recovery, etc. This highlights the need for effective measures to safeguard healthcare systems against ransomware attacks.
Ransomware attacks pose a significant threat to the healthcare industry, and the consequences can be dire.
- Telegram Fraud: A Rising Concern in 2023

The article discusses the increasing trend of Telegram fraud, which refers to malicious or deceitful activities on the Telegram messaging app, and how cybercriminals use it to steal valuable data from businesses and consumers. The article explains how criminals use bots or people to deceive users into doing something they wouldn’t normally do by creating fake profiles, conducting phishing scams, deploying malware, and promoting fake investment and charity scams. The article also explains why Telegram and other messaging apps have become appealing to criminals, as they provide an easy and quick way to steal money and are borderless. The article concludes by offering tips on how to prevent Telegram fraud and better protect businesses.
- Genesis Market Heist: Dutch Cybercriminal Arrested for Stealing €150,000

Dutch authorities have arrested a 28-year-old man from Maassluis, Netherlands, on charges of stealing €150,000 from at least 50 Dutch victims through the illegal online marketplace, Genesis Market. The man was arrested during an international police operation against the platform.
Genesis Market offered buyers access to login credentials, cookies, and other data from infected computers. The marketplace developed a separate browser and browser plug-in, allowing buyers to log in to various services with stolen credentials. Genesis Market promised to keep the stolen data up-to-date as long as it had access to the victim’s infected computer.
The suspect from Maassluis allegedly purchased data from at least 500 Dutch victims through Genesis Market for €10,000. He then used the stolen data to gain access to bank accounts and steal €150,000 from at least 50 victims. He also redirected victims’ phone numbers or took over their accounts using sim-swapping.
Sim-swapping is a method where cybercriminals transfer a victim’s phone number to a SIM card they control, preventing the victim from making calls, sending messages, or using mobile internet. This technique can provide access to two-factor authentication (2FA) codes.
The suspect from Maassluis has been charged with several offenses, including computer intrusion, data theft, and identity fraud. This arrest is a reminder of the risks of illegal marketplaces like Genesis Market and the importance of maintaining online security. It is essential to use strong, unique passwords and two-factor authentication to safeguard personal information and accounts from cybercriminals. Users must also remain vigilant and avoid sharing personal information or credentials with unknown sources.
Source: https://www.om.nl/actueel/nieuws/2023/04/07/verdachte-van-operatie-cookiemonster-in-bewaring
- Targeted User Surveillance with WindowSpy

WindowSpy is a Cobalt Strike Beacon Object File specifically designed for targeted user surveillance. Its primary objective is to enhance stealth during user surveillance by only triggering surveillance capabilities on specific targets such as confidential documents, browser login pages, VPN logins, among others. This not only saves time but also prevents detection of repeated use of surveillance capabilities, like screenshots. With WindowSpy, you can easily customize the list of strings to match your requirements, and the “spy()” function is highly adaptable to your preferences, allowing you to tailor your surveillance strategy as you see fit.
WindowSpy is a revolutionary tool designed to increase stealth during user surveillance by triggering surveillance capabilities only on certain targets, such as browser login pages, confidential documents, VPN logins, and more. This prevents detection of repeated use of surveillance capabilities like screenshots, and saves red teams time in sifting through excessive amounts of surveillance data produced by keylogging/screenwatch running at all times.
So how does WindowSpy work? Each time a beacon checks in, the BOF runs on the target. The BOF comes with a hardcoded list of strings that are common in useful window titles, such as “login,” “administrator,” “control panel,” “VPN,” and more. You can even customize this list and recompile the tool yourself to match your specific needs.
WindowSpy enumerates the visible windows and compares the titles to the list of strings. If any of these are detected, it triggers a local aggressorscript function defined in WindowSpy.cna named spy(). By default, it takes a screenshot, but you can customize this function to perform keylogging, WireTap, webcam access, and more.
Installation of WindowSpy is a breeze. Simply load the WindowSpy.cna script into Cobalt Strike and build from the source code, which can be easily accessed through the WindowSpy.sln solution file in Visual Studio. Then, leave it to run and it will automatically run on each beacon check-in and trigger accordingly.
WindowSpy was built by a developer who was bored and wanted to experiment with user surveillance. But don’t let its lighthearted origins fool you – this tool is incredibly powerful and highly effective. If you encounter any bugs or have any issues with the design, the developer encourages you to open an issue and they will work to resolve it.
If you’re looking for an innovative and customizable user surveillance tool, WindowSpy is the perfect solution. Try it today and experience the ultimate in targeted user monitoring.
- Securing SaaS with NIST’s Three-Pronged Approach and Contextual Data

The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is a leader in cybersecurity and has released a guide for securing enterprise network landscapes that emphasizes a three-pronged approach to security, focusing on the user, endpoint, and application. Effective security tools for Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) must be able to integrate seamlessly with SaaS applications and provide coverage for the entire SaaS stack. Automation is critical for securing the vast number of configurations, and tools must use contextual data to detect threats from humans and machines. Device management is also crucial for SaaS security, and access should be granted using a zero-trust approach. Effective SaaS security platforms follow NIST’s cybersecurity approach to monitor and track usage, users, and behaviors, as well as identify threats.
- Genesis Market Scandal: Dutch Victim Loses €70,000, 50,000 Others at Risk

Dutch victim loses €70,000 to Genesis Market: over 50,000 others may have been affected
One 71-year-old man in the Netherlands lost €70,000 to Genesis Market, which was recently shut down by law enforcement. The police suspect that as many as 50,000 other Dutch individuals may have also fallen victim to this illegal marketplace, which traded in personal information obtained via malware.
The elderly victim first became aware of the fraud when he received an SMS from a bank informing him that his phone number had been changed. Recognizing it as a likely scam, he ignored the message. However, a month later he received a letter from PostNL stating that all mail under his name would be redirected to a new address from 5th February 2021, with no further details provided.
After contacting PostNL’s customer service, he managed to cancel the redirection but was unable to find out who had requested it or where his mail would have been sent. The same month, he was shown a letter by a postman stating that his address should no longer be traced back to an Amsterdam location. Included in the post was a letter from the bank containing a pin code for a new account in his name.
Further investigation revealed that multiple bank accounts had been opened under his name, with one account being used to steal almost €70,000 from his investment account. He also discovered that various items had been purchased in his name from online retailers, although he did not receive the goods himself. Despite reporting the crimes to the police, it was not until a laptop was seized from a suspect that the full extent of the victim’s personal information was discovered.
Feeling overwhelmed and paranoid, the man took steps to protect himself by changing his phone number and internet provider. With the help of the police and a lawyer, he eventually recovered from the ordeal without further financial loss, apart from the fees for his legal representation and a new passport.
The Genesis Market incident serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of online fraud and the importance of staying vigilant and protecting personal information.
Source: https://www.politie.nl/nieuws/2023/april/6/peter-werd-slachtoffer-van-identiteitsfraude.html
- Best Practices for Handling Secrets in Jenkins

Jenkins is a widely used open-source automation server for continuous integration and deployment of software. To ensure the security and integrity of applications being built and deployed, it is crucial to manage secrets in Jenkins carefully. In this article, Keshav Malik, a full-time Security Engineer, discusses best practices for managing secrets in Jenkins, including configuring and managing secrets, and how to handle potential security breaches. The article also covers storing secrets with Hashicorp Vault and integrating it with Jenkins. It is essential to follow best practices when managing secrets, including using different secrets for different purposes, restricting their access, and regularly rotating and updating them.
- Securing Communication Channels: Importance of Communications Security (COMSEC) and Tools to Improve it

Communications security (COMSEC) is the practice of protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information exchanged through communication channels. As the world becomes more connected through the internet and other communication technologies, the need for effective COMSEC measures becomes more important than ever.
One of the most critical aspects of COMSEC is the use of encryption to protect data from being intercepted and read by unauthorized parties. Encryption involves transforming plaintext data into ciphertext, which can only be read by those who possess the correct decryption key. There are many encryption algorithms and protocols available, ranging from symmetric key encryption, where the same key is used for both encryption and decryption, to asymmetric key encryption, where a public key is used for encryption and a private key is used for decryption.
Enhancing Communication Security: Encryption Alone is Not Enough
However, encryption alone is not enough to ensure secure communication. Attackers may attempt to intercept communications, tamper with data, or launch other types of attacks to compromise the security of a communication channel. Therefore, additional measures such as authentication, access control, and traffic analysis are needed to provide comprehensive COMSEC.
There are many tools and techniques available to improve COMSEC. For example, GPG Sync is a tool that automates the distribution and management of OpenPGP public keys, ensuring that everyone in an organization has access to the correct keys for secure communication. Geneva (Genetic Evasion) is a novel genetic algorithm that can evolve packet-manipulation-based censorship evasion strategies to evade nation-state-level censors and increase the availability of otherwise blocked content.
Enhancing COMSEC through encryption and security tools
GlobaLeaks and SecureDrop are both tools that enable whistleblowers to securely and anonymously submit sensitive information to media organizations and NGOs. These tools provide a secure and private way for individuals to share information without fear of retribution.
Teleport is a tool that allows engineers and security professionals to unify access for various systems and applications, providing a comprehensive solution for managing access control and authentication across multiple environments.
In conclusion, COMSEC is a critical aspect of modern communication, and the use of encryption and other security measures is essential to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. With the help of tools such as GPG Sync, Geneva, GlobaLeaks, SecureDrop, and Teleport, organizations can improve their COMSEC and reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents.
You can find GPG Sync at https://github.com/firstlookmedia/gpgsync, Geneva at https://censorship.ai, GlobaLeaks at https://www.globaleaks.org, SecureDrop at https://securedrop.org, and Teleport at https://goteleport.com.
- ChatGPT: The Star Trek Computer Come to Life

The idea of a sentient computer capable of understanding and responding to human speech has been a popular topic in science fiction for decades. One such example is the character of “Computer” from the Star Trek franchise. While the concept of a sentient computer may have once seemed like pure fiction, today’s AI language models are bringing us closer to that reality than ever before. We will explore how ChatGPT, a language model based on the GPT-3.5 architecture, shares some similarities with the Star Trek Computer. We will discuss how both ChatGPT and the Star Trek Computer are able to process vast amounts of information, interpret natural language commands, and learn and adapt over time. While there are certainly some differences between ChatGPT and the Star Trek Computer, the similarities are intriguing and offer a glimpse into the potential future of AI technology.
Comparing AI to Star Trek’s sentient computer
As an AI language model, ChatGPT shares some similarities with the character of “Computer” from Star Trek. The concept of a sentient computer capable of understanding and responding to human speech has been a staple of science fiction for decades, and the portrayal of the Computer in Star Trek offers an interesting comparison to the capabilities of ChatGPT.
Firstly, like the Computer on the USS Enterprise, ChatGPT is capable of processing vast amounts of information at incredible speeds. With access to the internet and a huge database of knowledge, ChatGPT can quickly and accurately answer a wide range of questions on a variety of subjects. This ability to retrieve and analyze data is a key aspect of the Computer’s role on the Enterprise, and it is a capability that ChatGPT shares.
Natural Language and Learning
Furthermore, both ChatGPT and the Star Trek Computer are able to interpret and respond to natural language commands. In the Star Trek universe, characters are able to speak to the Computer in a conversational manner, using normal speech patterns rather than complex code or programming languages. Similarly, users can interact with ChatGPT using natural language, without needing to learn any specialized syntax or programming.
Another similarity between ChatGPT and the Star Trek Computer is their ability to learn and adapt. The Computer on the Enterprise is able to learn and improve its performance over time, becoming more efficient and effective at its tasks. Similarly, ChatGPT is continually being trained and updated with new information and techniques, allowing it to improve its responses and better understand the nuances of human language.
Differences in Form, Not Function
Of course, there are also some differences between ChatGPT and the Star Trek Computer. For one, ChatGPT does not have a physical presence or a voice of its own, unlike the Computer on the Enterprise. However, this difference is largely a matter of aesthetics and design, rather than a fundamental difference in functionality.
In conclusion, while ChatGPT is not an exact replica of the Computer from Star Trek, there are certainly some similarities between the two. Both are highly advanced AI systems capable of processing vast amounts of information, interpreting natural language commands, and learning and adapting over time. As AI technology continues to develop, it will be interesting to see how closely these fictional portrayals of sentient computers align with the real-world capabilities of AI language models like ChatGPT.
- Vulnerabilities and Insights: A Look at Cybersecurity Challenges

The blog discusses cybersecurity challenges that organizations face in the rapidly evolving digital landscape. The sheer volume of vulnerabilities and cyber risks can be overwhelming for companies to manage effectively. Organizations can gain valuable insights that help them mitigate risks and make informed decisions by analyzing data points. The blog suggests cataloging vulnerabilities, prioritizing them based on risk, evaluating the root cause of vulnerabilities, and developing a remediation plan. The blog also recommends staying up to date with the latest research and trends in the industry to stay informed and ahead of the curve when it comes to cyber threats.
- 50,000 Dutch Citizens Fall Victim to Genesis Market Cyber Attack: Is Your Account Safe?

In a major operation against the illegal online marketplace Genesis Market, the Dutch police have arrested 17 suspects and searched 23 homes, while also suspecting that 50,000 Dutch citizens have fallen victim to the malware spread by the cyber criminals. The police are now urging Dutch citizens to check whether their accounts were traded via the marketplace on the website police.nl/checkjehack. Worldwide, the operation has led to 119 arrests and 208 searches, with two million infected computers estimated, including the 50,000 in the Netherlands.
The FBI recently seized Genesis Market, with Dutch police also involved in the operation. The marketplace offered login details, cookies, and other data from infected computers, enabling buyers to log in to various services using stolen credentials. Genesis Market claimed that it would keep stolen data up to date as long as it had access to the victim’s infected computer, even if the victim created a new account. As antivirus company Sophos pointed out, Genesis Market customers did not buy one-time stolen data of unknown quality but paid for a subscription to a victim’s information, even as it changed.
Police investigations revealed that information from 1.5 million infected computers was traded, including 50,000 Dutch computers. Some victims were scammed out of money or had their social media profiles hijacked, while others lost their entire investment portfolios or had their bank accounts and cryptocurrency wallets emptied. One 71-year-old victim had almost €70,000 stolen from his investment account and found multiple bank accounts opened in his name.
The police advise victims not to change their passwords since the malware is designed to inform the cybercriminal of any updates. Instead, the police urge citizens to check whether their accounts were compromised and follow the instructions on the politie.nl/checkjehack website. This is a critical step that everyone must take since the cybercriminals are still at large. The police will also be releasing social media videos to raise awareness about the “Check Je Hack” campaign. Europol and the British police are also directing their citizens to use the Dutch police’s tool.
Sources:
https://www.politie.nl/nieuws/2023/april/5/operation-cookiemonster-nl.html
- Boost Your GitHub and GitLab Security with Legitify’s GPT-Powered Analysis Tool

Curious what #gpt3 has to say about your #github and #gitlab security posture? Legit Security’s open-source tool, “Legitify”, now allows you to use OpenAI GPT’s capabilities to find GitHub and GitLab misconfigurations. Try the
legitify gpt-analysiscommand to get GPT-based security recommendations for your #github/ #gitlab assets.Legit Security’s Legitify tool is a powerful open-source solution for evaluating the security posture of your GitHub and GitLab assets. With the integration of OpenAI’s GPT-3 language model, Legitify now offers even more advanced capabilities to identify misconfigurations in your code repositories. By simply running the legitify gpt-analysis command, users can receive comprehensive security recommendations based on GPT’s powerful natural language processing abilities. This innovative tool enables developers and security teams to proactively identify and address potential vulnerabilities in their codebase, helping to improve the overall security of their software assets. Whether you’re a solo developer or part of a larger team, Legitify is an essential tool for anyone looking to maintain a robust and secure code repository.
- Navigating the Seven Seas of Vulnerability Management: A Comprehensive Guide

The article discusses the seven stages of the vulnerability management lifecycle. The first step is consolidation, where centralizing the cyber risk data is necessary for complete visibility, duplicate data management, and better control. The second step is correlation, where vulnerability deduplication and clustering is essential for simplified scan data management, accurate risk understanding, and improved operating efficiency. The third step is enrichment, where correlated scan data is enriched with actionable information like threat intelligence sources, root cause analysis, remediation intelligence, and attacker path context. The fourth step is prioritization, where identified, correlated, and enriched vulnerabilities are organized into a prioritized list that matches the risk-based policies of an organization. The fifth step is orchestration, where the entire mitigation operation is orchestrated efficiently through automation. The sixth step is collaboration, where all stakeholders involved in vulnerability management communicate and collaborate effectively to streamline risk mitigation. The last step is reporting, where organizations report on their progress to demonstrate the effectiveness of their vulnerability management program.
- Nebu Ordered to Disclose Cyber Attack Details in Court Ruling: A Wake-Up Call for Businesses

In a recent court ruling in Rotterdam, Dutch software provider Nebu has been ordered to provide market research firm Blauw with information regarding a cyber attack on its systems and the resulting data theft. If Nebu fails to comply with this ruling, it will face penalties of up to €500,000. Blauw uses Nebu’s solutions for conducting market research on behalf of its clients.
In March, hackers breached Nebu’s servers, stealing data in the process. Blauw argued that it did not receive sufficient information from Nebu regarding the attack, its aftermath, and the steps taken by Nebu. As a result, Blauw filed a lawsuit demanding detailed information and an independent forensic investigation.
The court ruled in favor of Blauw, ordering Nebu to provide extensive information on the breach, including how the attackers gained access and their actions while on the systems. Nebu must also share all available information on the stolen data and the attackers, while being mindful of potentially sensitive information. The court also imposed penalties for non-compliance and awarded Blauw €2,400 in costs.
So far, 139 organizations have reported the Nebu data breach to the Dutch Data Protection Authority.
- Free IoT Tool for Finding Zero-Day Vulnerabilities

A new Free Plan for a security tool has been launched, offering full functionality with no limitations on zero-day vulnerability discovery and firmware analysis. The tool is aimed at security professionals, developers, and bug bounty hunters who can use it to gain a competitive advantage. The creators hope to remove financial barriers for security professionals and receive feedback to improve the tool’s features. The Free Plan will remain free, and users can expect to see updates based on their feedback.
- The Art of Selling Security: How to Convince Your CFO to Invest in Your Business’s Protection

The article provides a guide on how to propose a security investment to your CFO, addressing why it is challenging to pitch security to a CFO and what things the CFO wants to see. CFOs are busy people and managing budgets that seem to get smaller while the ask for spending becomes more frequent. The value a security investment brings to the organization is what CFOs generally look at when evaluating if something is “valuable” to their organization. These include reduced costs, reduced risks, increased productivity, and increased growth (mostly for revenue). The article provides a budget request template to make the ask even easier.
- Exploring the Dark Side of ChatGPT: Uncovering the Malicious Use of AI

Checkpoint’s manager of threat intelligence, Sergey Shykevich, expressed concern about the malicious use of ChatGPT, an AI tool that can generate written content. Checkpoint conducted research to build a full malicious infection chain using OpenAI and discovered that cybercriminals have started using ChatGPT to build malicious tools. While ChatGPT is a great tool, Shykevich warns that it is important to specify exactly what you need and that ChatGPT code is far from perfect. Cybercriminals are still trying to understand how it works, and the generated code is rough. Nevertheless, Shykevich warns that ChatGPT combines code with the program, making it easier for cybercriminals to create malware using one interface.